Intrinsic protein disorder in human pathways
- PMID: 22012032
- PMCID: PMC3584708
- DOI: 10.1039/c1mb05274h
Intrinsic protein disorder in human pathways
Abstract
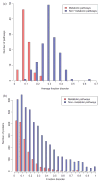
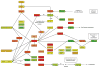
We analyze human-specific KEGG pathways trying to understand the functional role of intrinsic disorder in proteins. Pathways provide a comprehensive picture of biological processes and allow better understanding of a protein's function within the specific context of its surroundings. Our study pinpoints a few specific pathways significantly enriched in disorder-containing proteins and identifies the role of these proteins within the framework of pathway relationships. Three major categories of relations are shown to be significantly enriched in disordered proteins: gene expression, protein binding and to a lesser degree, protein phosphorylation. Finally we find that relations involving protein activation and to some extent inhibition are characterized by low disorder content.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

