Abdominal adiposity, insulin and bone quality in young male rats fed a high-fat diet containing soybean or canola oil
- PMID: 22012056
- PMCID: PMC3180158
- DOI: 10.1590/s1807-59322011001000022
Abdominal adiposity, insulin and bone quality in young male rats fed a high-fat diet containing soybean or canola oil
Abstract
Objectives: A low ratio of omega-6/omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is associated with healthy bone properties. However, fatty diets can induce obesity. Our objective was to evaluate intra-abdominal adiposity, insulin, and bone growth in rats fed a high-fat diet containing low ratios of omega-6/omega-3 provided in canola oil.
Methods: After weaning, rats were grouped and fed either a control diet (7S), a high-fat diet containing soybean oil (19S) or a high-fat diet of canola oil (19C) until they were 60 days old. Differences were considered to be significant if p<0.05.
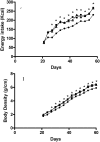
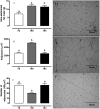
Results: After 60 days, the 19S and 19C groups showed more energy intake, body density growth and intraabdominal fat mass. However, the 19S group had a higher area (200%) and a lower number (44%) of adipocytes, while the 7S and 19C groups did not differ. The serum concentrations of glucose and insulin and the insulin resistance index were significantly increased in the 19C group (15%, 56%, and 78%, respectively) compared to the 7S group. Bone measurements of the 19S and 19C groups showed a higher femur mass (25%) and a higher lumbar vertebrae mass (11%) and length (5%). Computed tomography analysis revealed more radiodensity in the proximal femoral epiphysis and lumbar vertebrae of 19C group compared to the 7S and 19S groups.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the amount and source of fat used in the diet after weaning increase body growth and fat depots and affect insulin resistance and, consequently, bone health.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

