Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1A: a key regulator of cardiac fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix remodeling in the heart
- PMID: 22012077
- PMCID: PMC4114346
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-011-0228-2
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1A: a key regulator of cardiac fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix remodeling in the heart
Abstract
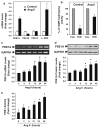
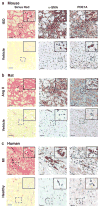
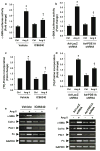
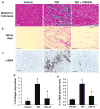
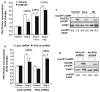
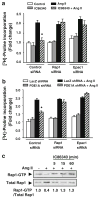
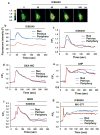
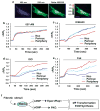
Cardiac fibroblasts become activated and differentiate to smooth muscle-like myofibroblasts in response to hypertension and myocardial infarction (MI), resulting in extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, scar formation and impaired cardiac function. cAMP and cGMP-dependent signaling have been implicated in cardiac fibroblast activation and ECM synthesis. Dysregulation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity/expression is also associated with various diseases and several PDE inhibitors are currently available or in development for treating these pathological conditions. The objective of this study is to define and characterize the specific PDE isoform that is altered during cardiac fibroblast activation and functionally important for regulating myofibroblast activation and ECM synthesis. We have found that Ca(2+)/calmodulin-stimulated PDE1A isoform is specifically induced in activated cardiac myofibroblasts stimulated by Ang II and TGF-β in vitro as well as in vivo within fibrotic regions of mouse, rat, and human diseased hearts. Inhibition of PDE1A function via PDE1-selective inhibitor or PDE1A shRNA significantly reduced Ang II or TGF-β-induced myofibroblast activation, ECM synthesis, and pro-fibrotic gene expression in rat cardiac fibroblasts. Moreover, the PDE1 inhibitor attenuated isoproterenol-induced interstitial fibrosis in mice. Mechanistic studies revealed that PDE1A modulates unique pools of cAMP and cGMP, predominantly in perinuclear and nuclear regions of cardiac fibroblasts. Further, both cAMP-Epac-Rap1 and cGMP-PKG signaling was involved in PDE1A-mediated regulation of collagen synthesis. These results suggest that induction of PDE1A plays a critical role in cardiac fibroblast activation and cardiac fibrosis, and targeting PDE1A may lead to regression of the adverse cardiac remodeling associated with various cardiac diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vinpocetine Attenuates Pathological Cardiac Remodeling by Inhibiting Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017 Apr;31(2):157-166. doi: 10.1007/s10557-017-6719-0. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017. PMID: 28321644 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 1 in mediating cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.Circ Res. 2009 Nov 6;105(10):956-64. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.198515. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19797176 Free PMC article.
-
The PDE1A-PKCalpha signaling pathway is involved in the upregulation of alpha-smooth muscle actin by TGF-beta1 in adventitial fibroblasts.J Vasc Res. 2010;47(1):9-15. doi: 10.1159/000231716. Epub 2009 Aug 6. J Vasc Res. 2010. PMID: 19672103 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblasts and the extracellular matrix in right ventricular disease.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 Oct 1;113(12):1453-1464. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx146. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28957531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of mechanical factors in modulating cardiac fibroblast function and extracellular matrix synthesis.Cardiovasc Res. 2000 May;46(2):257-63. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(00)00030-4. Cardiovasc Res. 2000. PMID: 10773229 Review.
Cited by
-
An update on vinpocetine: New discoveries and clinical implications.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 15;819:30-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.11.041. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29183836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Therapeutic Strategies against Cardiac Fibrosis: From Classical Pharmacology to Novel Molecular, Epigenetic, and Biotechnological Approaches.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 8;24(8):226. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2408226. eCollection 2023 Aug. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of phosphodiesterase 1 in the pathophysiology of diseases and potential therapeutic opportunities.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Oct;226:107858. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107858. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33895190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vinpocetine Attenuates Pathological Cardiac Remodeling by Inhibiting Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017 Apr;31(2):157-166. doi: 10.1007/s10557-017-6719-0. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2017. PMID: 28321644 Free PMC article.
-
Redox signaling as a therapeutic target to inhibit myofibroblast activation in degenerative fibrotic disease.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:131737. doi: 10.1155/2014/131737. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24701562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batchelor AM, Bartus K, Reynell C, Constantinou S, Halvey EJ, Held KF, Dostmann WR, Vernon J, Garthwaite J. Exquisite sensitivity to subsecond, picomolar nitric oxide transients conferred on cells by guanylyl cyclase-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:22060–22065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013147107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bax NA, van Oorschot AA, Maas S, Braun J, van Tuyn J, de Vries AA, Groot AC, Goumans MJ. In vitro epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation in human adult epicardial cells is regulated by TGFbeta-signaling and WT1. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106:829–847. doi: 10.1007/s00395-011-0181-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

