Murein and pseudomurein cell wall binding domains of bacteria and archaea--a comparative view
- PMID: 22012341
- PMCID: PMC3210951
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-011-3637-0
Murein and pseudomurein cell wall binding domains of bacteria and archaea--a comparative view
Abstract
The cell wall, a major barrier protecting cells from their environment, is an essential compartment of both bacteria and archaea. It protects the organism from internal turgor pressure and gives a defined shape to the cell. The cell wall serves also as an anchoring surface for various proteins and acts as an adhesion platform for bacteriophages. The walls of bacteria and archaea are mostly composed of murein and pseudomurein, respectively. Cell wall binding domains play a crucial role in the non-covalent attachment of proteins to cell walls. Here, we give an overview of the similarities and differences in the biochemical and functional properties of the two major murein and pseudomurein cell wall binding domains, i.e., the Lysin Motif (LysM) domain (Pfam PF01476) and the pseudomurein binding (PMB) domain (Pfam PF09373) of bacteria and archaea, respectively.
Figures
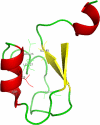
References
-
- Arrighi JF, Barre A, Ben Amor B, Bersoult A, Soriano LC, Mirabella R, de Carvalho-Niebel F, Journet EP, Gherardi M, Huguet T, Geurts R, Denarie J, Rouge P, Gough C. The Medicago truncatula lysin motif-receptor-like kinase gene family includes NFP and new nodule-expressed genes. Plant Physiol. 2006;142:265–279. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.084657. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

