Oncogenic ETS proteins mimic activated RAS/MAPK signaling in prostate cells
- PMID: 22012618
- PMCID: PMC3205585
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.17546311
Oncogenic ETS proteins mimic activated RAS/MAPK signaling in prostate cells
Abstract
The aberrant expression of an oncogenic ETS transcription factor is implicated in the progression of the majority of prostate cancers, 40% of melanomas, and most cases of gastrointestinal stromal tumor and Ewing's sarcoma. Chromosomal rearrangements in prostate cancer result in overexpression of any one of four ETS transcription factors. How these four oncogenic ETS genes differ from the numerous other ETS genes expressed in normal prostate and contribute to tumor progression is not understood. We report that these oncogenic ETS proteins, but not other ETS factors, enhance prostate cell migration. Genome-wide binding analysis matched this specific biological function to occupancy of a unique set of genomic sites highlighted by the presence of ETS- and AP-1-binding sequences. ETS/AP-1-binding sequences are prototypical RAS-responsive elements, but oncogenic ETS proteins activated a RAS/MAPK transcriptional program in the absence of MAPK activation. Thus, overexpression of oncogenic ETS proteins can replace RAS/MAPK pathway activation in prostate cells. The genomic description of this ETS/AP-1-regulated, RAS-responsive, gene expression program provides a resource for understanding the role of these ETS factors in both an oncogenic setting and the developmental processes where these genes normally function.
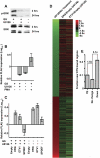
Figures
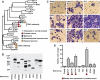
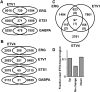
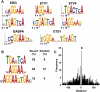
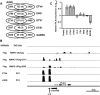

References
-
- Baert JL, Beaudoin C, Monte D, Degerny C, Mauen S, de Launoit Y 2007. The 26S proteasome system degrades the ERM transcription factor and regulates its transcription-enhancing activity. Oncogene 26: 415–424 - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 2: 28–36 - PubMed
-
- Bello D, Webber MM, Kleinman HK, Wartinger DD, Rhim JS 1997. Androgen responsive adult human prostatic epithelial cell lines immortalized by human papillomavirus 18. Carcinogenesis 18: 1215–1223 - PubMed
-
- Bonaccorsi L, Nesi G, Nuti F, Paglierani M, Krausz C, Masieri L, Serni S, Proietti-Pannunzi L, Fang Y, Jhanwar SC, et al. 2009. Persistence of expression of the TMPRSS2:ERG fusion gene after pre-surgery androgen ablation may be associated with early prostate specific antigen relapse of prostate cancer: preliminary results. J Endocrinol Invest 32: 590–596 - PubMed
-
- Bos JL 1989. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res 49: 4682–4689 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
