The Cyclin K/Cdk12 complex maintains genomic stability via regulation of expression of DNA damage response genes
- PMID: 22012619
- PMCID: PMC3205586
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.16962311
The Cyclin K/Cdk12 complex maintains genomic stability via regulation of expression of DNA damage response genes
Abstract
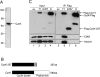
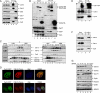
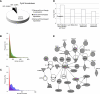
Various cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) complexes have been implicated in the regulation of transcription. In this study, we identified a 70-kDa Cyclin K (CycK) that binds Cdk12 and Cdk13 to form two different complexes (CycK/Cdk12 or CycK/Cdk13) in human cells. The CycK/Cdk12 complex regulates phosphorylation of Ser2 in the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II and expression of a small subset of human genes, as revealed in expression microarrays. Depletion of CycK/Cdk12 results in decreased expression of predominantly long genes with high numbers of exons. The most prominent group of down-regulated genes are the DNA damage response genes, including the critical regulators of genomic stability: BRCA1 (breast and ovarian cancer type 1 susceptibility protein 1), ATR (ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related), FANCI, and FANCD2. We show that CycK/Cdk12, rather than CycK/Cdk13, is necessary for their expression. Nuclear run-on assays and chromatin immunoprecipitations with RNA polymerase II on the BRCA1 and FANCI genes suggest a transcriptional defect in the absence of CycK/Cdk12. Consistent with these findings, cells without CycK/Cdk12 induce spontaneous DNA damage and are sensitive to a variety of DNA damage agents. We conclude that through regulation of expression of DNA damage response genes, CycK/Cdk12 protects cells from genomic instability. The essential role of CycK for organisms in vivo is further supported by the result that genetic inactivation of CycK in mice causes early embryonic lethality.
Figures




Comment in
-
The cyclin K/Cdk12 complex: an emerging new player in the maintenance of genome stability.Cell Cycle. 2012 Mar 15;11(6):1049-50. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.6.19678. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22391210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahn SH, Kim M, Buratowski S 2004. Phosphorylation of serine 2 within the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain couples transcription and 3′ end processing. Mol Cell 13: 67–76 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
