Prox1 dosage controls the number of lymphatic endothelial cell progenitors and the formation of the lymphovenous valves
- PMID: 22012621
- PMCID: PMC3205588
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.16974811
Prox1 dosage controls the number of lymphatic endothelial cell progenitors and the formation of the lymphovenous valves
Abstract
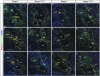
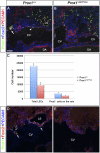
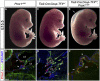
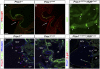
Arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels are functionally linked, and their physical interaction is tightly regulated. The lymphatic vessels communicate with the blood vessels only at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins. Here, we characterize the embryonic lymphovenous valves controlling this vital communication and show that they are formed by the intercalation of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) with a subpopulation of venous endothelial cells (ECs) at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins. We found that unlike LEC progenitors, which move out from the veins and differentiate into mature LECs, these Prox1-expressing ECs remain in the veins and do not acquire LEC features. We demonstrate that the development of this Prox1-expressing venous EC population, and therefore of lymphovenous valves, requires two functional copies of Prox1, as the valves are absent in Prox1 heterozygous mice. We show that this is due to a defect in the maintenance of Prox1 expression in venous ECs and LEC progenitors promoted by a reduction in Coup-TFII/Prox1 complex formation. This is the first report describing the molecular mechanism controlling lymphovenous communication.
Figures



References
-
- Copeland RA 2000. Enzymes: a practical introduction to structure, mechanism and data analysis. Wiley-VCH, New York
-
- Dekker RJ, van Soest S, Fontijn RD, Salamanca S, de Groot PG, VanBavel E, Pannekoek H, Horrevoets AJ 2002. Prolonged fluid shear stress induces a distinct set of endothelial cell genes, most specifically lung Kruppel-like factor (KLF2). Blood 100: 1689–1698 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
