Hippocampal contributions to the processing of social emotions
- PMID: 22012639
- PMCID: PMC3340463
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21485
Hippocampal contributions to the processing of social emotions
Abstract
Inducing and experiencing emotions about others' mental and physical circumstances is thought to involve self-relevant processing and personal memories of similar experiences. The hippocampus is important for self-referential processing during recall and prospection; however, its contributions during social emotions have not been systematically investigated. We use event-related averaging and Granger causal connectivity mapping to investigate hippocampal contributions during the processing of varieties of admiration and compassion pertaining to protagonists' mental versus physical circumstances [admiration for virtue (AV) versus for skill; compassion for social/psychological pain (CSP) versus for physical pain]. Data were collected using a multistep emotion-induction paradigm that included psychosocial interviews, BOLD fMRI, and simultaneous psychophysiological recording. Given that mnemonic demands were equivalent among conditions, we tested whether: (1) the hippocampi would be recruited more strongly and for a longer duration during the processing of AV and CSP; and (2) connectivity between the hippocampi and cortical systems involved in visceral somatosensation/emotional feeling, social cognitive, and self-related processing would be more extensive during AV and CSP. Results elucidate the hippocampus' facilitative role in inducing and sustaining appropriate emotional reactions, the importance of self-related processing during social emotions, and corroborate the conception that varieties of emotional processing pertaining to others' mental and physical situations engage at least partially distinct neural mechanisms.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
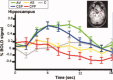
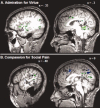

References
-
- Ames DL, Jenkins AC, Banaji MR, Mitchell JP ( 2008): Taking another person's perspective increases self‐referential neural processing. Psychol Sci 19: 642–644. - PubMed
-
- Amodio DM, Frith CD ( 2006): Meeting of minds: The medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 7: 268–277. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y ( 1995): Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J Roy Stat Soc Series B: Methodological 57: 289–300.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

