Dendrimer-mediated multivalent binding for the enhanced capture of tumor cells
- PMID: 22012872
- PMCID: PMC3549433
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201105508
Dendrimer-mediated multivalent binding for the enhanced capture of tumor cells
Figures


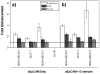
References
-
- Hong S, Leroueil PR, Majoros IJ, Orr BG, Baker JR, Jr, Banaszak Holl MM. Chem Biol. 2007;14:107. - PubMed
- Kiessling LL, Pohl NL. Chem Biol. 1996;3:71. - PubMed
- Quintana A, Raczka E, Piehler L, Lee I, Myc A, Majoros I, Patri AK, Thomas T, Mule J, Baker JR., Jr Pharm Res. 2002;19:1310. - PubMed
- Peer D, Karp JM, Hong S, Farokhzad OC, Margalit R, Langer R. Nat Nanotechnol. 2007;2:751. - PubMed
- Weissleder R, Kelly K, Sun EY, Shtatland T, Josephson L. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23:1418. - PubMed
-
- Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith MR, Kwak EL, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky A, Ryan P, Balis UJ, Tompkins RG, Haber DA, Toner M. Nature. 2007;450:1235. - PMC - PubMed
- Wang S, Wang H, Jiao J, Chen KJ, Owens GE, Kamei K, Sun J, Sherman DJ, Behrenbruch CP, Wu H, Tseng HR. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48:8970. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stott SL, Hsu CH, Tsukrov DI, Yu M, Miyamoto DT, Waltman BA, Rothenberg SM, Shah AM, Smas ME, Korir GK, Floyd FP, Jr, Gilman AJ, Lord JB, Winokur D, Springer S, Irimia D, Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Lee RJ, Isselbacher KJ, Maheswaran S, Haber DA, Toner M. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:18392. - PMC - PubMed
- Wang S, Liu K, Liu J, Yu ZT, Xu X, Zhao L, Lee T, Lee EK, Reiss J, Lee YK, Chung LW, Huang J, Rettig M, Seligson D, Duraiswamy KN, Shen CK, Tseng HR. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2011;50:3084. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

