Sustained inhibition of progressive joint damage with rituximab plus methotrexate in early active rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year results from the randomised controlled trial IMAGE
- PMID: 22012969
- PMCID: PMC3277723
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200170
Sustained inhibition of progressive joint damage with rituximab plus methotrexate in early active rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year results from the randomised controlled trial IMAGE
Abstract
Background: In the IMAGEstudy, rituximab plus methotrexate (MTX) inhibited joint damage and improved clinical outcomes at 1 year in MTX-naïve patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis.
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess joint damage progression and clinical outcomes over 2 years.
Methods: Patients (n=755) were randomised to receive rituximab 2×500 mg+MTX, 2×1000 mg+MTX or placebo+MTX. The placebo-controlled period continued to week 104. Two-year end points were defined as secondary or exploratory and included change in total Genant-modified Sharp score (mTSS), total erosion score and joint space narrowing score from baseline to week 104. Clinical efficacy and physical function end points were also assessed.
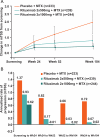
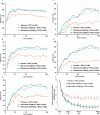
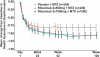
Results: At 2 years, rituximab 2×1000 mg+MTX maintained inhibition of progressive joint damage versus MTX alone (mTSS change 0.41 vs 1.95; p<0.0001 (79% inhibition)), and a higher proportion of patients receiving rituximab 2×1000 mg+MTX had no radiographic progression over 2 years compared with those receiving MTX alone (57% vs 37%; p<0.0001). Contrary to 1-year results, exploratory analysis of rituximab 2×500 mg+MTX at 2 years showed that progressive joint damage was slowed by ∼61% versus placebo+MTX (mTSS, exploratory p=0.0041). Improvements in clinical signs and symptoms and physical function seen after 1 year in rituximab-treated patients versus those receiving placebo were maintained at year 2. Safety profiles were similar between groups.
Conclusions: Treatment with rituximab 2×1000 mg+MTX was associated with sustained improvements in radiographic, clinical and functional outcomes over 2 years. Clinical trials.gov identifier NCT00299104.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
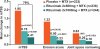
References
-
- Yelin E, Trupin L, Wong B, et al. The impact of functional status and change in functional status on mortality over 18 years among persons with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 2002;29:1851–7 - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Michaud K, Gefeller O, et al. Predicting mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:1530–42 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

