Shedding new light on opsin evolution
- PMID: 22012981
- PMCID: PMC3223661
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2011.1819
Shedding new light on opsin evolution
Abstract
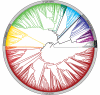
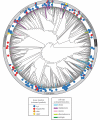
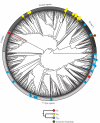
Opsin proteins are essential molecules in mediating the ability of animals to detect and use light for diverse biological functions. Therefore, understanding the evolutionary history of opsins is key to understanding the evolution of light detection and photoreception in animals. As genomic data have appeared and rapidly expanded in quantity, it has become possible to analyse opsins that functionally and histologically are less well characterized, and thus to examine opsin evolution strictly from a genetic perspective. We have incorporated these new data into a large-scale, genome-based analysis of opsin evolution. We use an extensive phylogeny of currently known opsin sequence diversity as a foundation for examining the evolutionary distributions of key functional features within the opsin clade. This new analysis illustrates the lability of opsin protein-expression patterns, site-specific functionality (i.e. counterion position) and G-protein binding interactions. Further, it demonstrates the limitations of current model organisms, and highlights the need for further characterization of many of the opsin sequence groups with unknown function.
Figures



References
-
- Marmor M. F., Martin L. J. 1978. 100 years of the visual cycle. Survey of Ophthalmology 22, 279–285 10.1016/0039-6257(78)90074-7 (doi:10.1016/0039-6257(78)90074-7) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wald G. 1967. George Wald Nobel Prize Lecture. In Nobel lectures, physiology or medicine 2963-1970. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Publishing Company
-
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. 1983. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron–exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell 34, 807–814 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8 (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zuker C. S., Cowman A. F., Rubin G. M. 1985. Isolation and structure of a rhodopsin gene from D. melanogaster. Cell 40, 851–858 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7 (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(85)90344-7) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arendt D. 2003. Evolution of eyes and photoreceptor cell types. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 47, 563–571 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
