Elevated glucose represses liver glucokinase and induces its regulatory protein to safeguard hepatic phosphate homeostasis
- PMID: 22013014
- PMCID: PMC3219956
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-0061
Elevated glucose represses liver glucokinase and induces its regulatory protein to safeguard hepatic phosphate homeostasis
Abstract
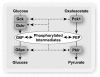
Objective: The induction of hepatic glucose 6-phosphatase (G6pc) by glucose presents a paradox of glucose-induced glucose intolerance. We tested whether glucose regulation of liver gene expression is geared toward intracellular homeostasis.
Research design and methods: The effect of glucose-induced accumulation of phosphorylated intermediates on expression of glucokinase (Gck) and its regulator Gckr was determined in hepatocytes. Cell ATP and uric acid production were measured as indices of cell phosphate homeostasis.
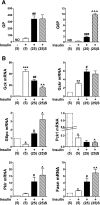
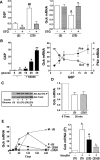
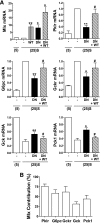
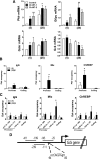
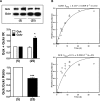
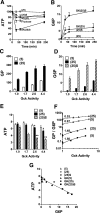
Results: Accumulation of phosphorylated intermediates in hepatocytes incubated at elevated glucose induced rapid and inverse changes in Gck (repression) and Gckr (induction) mRNA concomitantly with induction of G6pc, but had slower effects on the Gckr-to-Gck protein ratio. Dynamic metabolic labeling in mice and liver proteome analysis confirmed that Gckr and Gck are low-turnover proteins. Involvement of Max-like protein X in glucose-mediated Gck-repression was confirmed by chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis. Elevation of the Gck-to-Gckr ratio in hepatocytes was associated with glucose-dependent ATP depletion and elevated urate production confirming compromised phosphate homeostasis.
Conclusions: The lowering by glucose of the Gck-to-Gckr ratio provides a potential explanation for the impaired hepatic glucose uptake in diabetes. Elevated uric acid production at an elevated Gck-to-Gckr ratio supports a role for glucose regulation of gene expression in hepatic phosphate homeostasis.
Figures

References
-
- Agius L. Glucokinase and molecular aspects of liver glycogen metabolism. Biochem J 2008;414:1–18 - PubMed
-
- Agius L, Peak M, Newgard CB, Gomez-Foix AM, Guinovart JJ. Evidence for a role of glucose-induced translocation of glucokinase in the control of hepatic glycogen synthesis. J Biol Chem 1996;271:30479–30486 - PubMed
-
- Van Schaftingen E. Glycolysis revisited. Diabetologia 1993;36:581–588 - PubMed
-
- de la Iglesia N, Mukhtar M, Seoane J, Guinovart JJ, Agius L. The role of the regulatory protein of glucokinase in the glucose sensory mechanism of the hepatocyte. J Biol Chem 2000;275:10597–10603 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

