High-resolution profiling and analysis of viral and host small RNAs during human cytomegalovirus infection
- PMID: 22013051
- PMCID: PMC3255895
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.05903-11
High-resolution profiling and analysis of viral and host small RNAs during human cytomegalovirus infection
Abstract
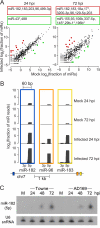
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) contributes its own set of microRNAs (miRNAs) during lytic infection of cells, likely fine-tuning conditions important for viral replication. To enhance our understanding of this component of the HCMV-host transcriptome, we have conducted deep-sequencing analysis of small RNAs (smRNA-seq) from infected human fibroblast cells. We found that HCMV-encoded miRNAs accumulate to ∼20% of the total smRNA population at late stages of infection, and our analysis led to improvements in viral miRNA annotations and identification of two novel HCMV miRNAs, miR-US22 and miR-US33as. Both of these miRNAs were capable of functionally repressing synthetic targets in transient transfection experiments. Additionally, through cross-linking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) of Argonaute (Ago)-bound RNAs from infected cells, followed by high-throughput sequencing, we have obtained direct evidence for incorporation of all HCMV miRNAs into the endogenous host silencing machinery. Surprisingly, three HCMV miRNA precursors exhibited differential incorporation of their mature miRNA arms between Ago2 and Ago1 complexes. Host miRNA abundances were also affected by HCMV infection, with significant upregulation observed for an miRNA cluster containing miR-96, miR-182, and miR-183. In addition to miRNAs, we also identified novel forms of virus-derived smRNAs, revealing greater complexity within the smRNA population during HCMV infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Cytomegalovirus miR-US33as-5p Targets IFNAR1 to Achieve Immune Evasion During Both Lytic and Latent Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 5;12:628364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.628364. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33746965 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus latent infection alters the expression of cellular and viral microRNA.Gene. 2014 Feb 25;536(2):272-8. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24361963
-
Comprehensive analysis of human cytomegalovirus microRNA expression during lytic and quiescent infection.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 12;9(2):e88531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088531. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24533100 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of host and viral microRNAs in human cytomegalovirus biology.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):180-92. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.10.011. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20969901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs expressed by human cytomegalovirus.Virol J. 2020 Mar 12;17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-1296-4. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 32164742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using next-generation sequencing of microRNAs to identify host and/or pathogen nucleic acid signatures in samples from children with biliary atresia - a pilot study.Access Microbiol. 2020 Jun 12;2(7):acmi000127. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000127. eCollection 2020. Access Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32974591 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved miRNA-183 cluster regulates the innate antiviral response.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 20;294(51):19785-19794. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010858. Epub 2019 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31694919 Free PMC article.
-
In-depth profiling and analysis of host and viral microRNAs in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) infected with megalocytivirus reveal involvement of microRNAs in host-virus interaction in teleost fish.BMC Genomics. 2014 Oct 8;15(1):878. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-878. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25297525 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNAs miR-US5-1 and miR-UL112-3p Block Proinflammatory Cytokine Production in Response to NF-κB-Activating Factors through Direct Downregulation of IKKα and IKKβ.mBio. 2017 Mar 7;8(2):e00109-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00109-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28270578 Free PMC article.
-
ARGONAUTE2 cooperates with SWI/SNF complex to determine nucleosome occupancy at human Transcription Start Sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 18;43(3):1498-512. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1387. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25605800 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

