Sequestration of phosphoinositides by mutated MARCKS effector domain inhibits stimulated Ca(2+) mobilization and degranulation in mast cells
- PMID: 22013076
- PMCID: PMC3237632
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-07-0614
Sequestration of phosphoinositides by mutated MARCKS effector domain inhibits stimulated Ca(2+) mobilization and degranulation in mast cells
Abstract
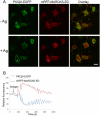
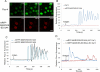
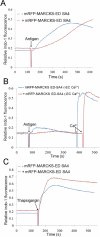
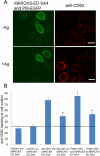
Protein kinase C β (PKCβ) participates in antigen-stimulated mast cell degranulation mediated by the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E, FcεRI, but the molecular basis is unclear. We investigated the hypothesis that the polybasic effector domain (ED) of the abundant intracellular substrate for protein kinase C known as myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS) sequesters phosphoinositides at the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane until MARCKS dissociates after phosphorylation by activated PKC. Real-time fluorescence imaging confirms synchronization between stimulated oscillations of intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations and oscillatory association of PKCβ-enhanced green fluorescent protein with the plasma membrane. Similarly, MARCKS-ED tagged with monomeric red fluorescent protein undergoes antigen-stimulated oscillatory dissociation and rebinding to the plasma membrane with a time course that is synchronized with reversible plasma membrane association of PKCβ. We find that MARCKS-ED dissociation is prevented by mutation of four serine residues that are potential sites of phosphorylation by PKC. Cells expressing this mutated MARCKS-ED SA4 show delayed onset of antigen-stimulated Ca(2+) mobilization and substantial inhibition of granule exocytosis. Stimulation of degranulation by thapsigargin, which bypasses inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate production, is also substantially reduced in the presence of MARCKS-ED SA4, but store-operated Ca(2+) entry is not inhibited. These results show the capacity of MARCKS-ED to regulate granule exocytosis in a PKC-dependent manner, consistent with regulated sequestration of phosphoinositides that mediate granule fusion at the plasma membrane.
Figures


References
-
- Aderem A. The MARCKS brothers: a family of protein kinase C substrates. Cell. 1992;71:713–716. - PubMed
-
- Bai J, Tucker WC, Chapman ER. PIP2 increases the speed of response of synaptotagmin and steers its membrane-penetration activity toward the plasma membrane. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:36–44. - PubMed
-
- Blackshear PJ. The MARCKS family of cellular protein kinase C substrates. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:1501–1504. - PubMed
-
- Blank U, Rivera J. The ins and outs of IgE-dependent mast-cell exocytosis. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:266–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

