Binding of anti-SSA antibodies to apoptotic fetal cardiocytes stimulates urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)/uPA receptor-dependent activation of TGF-β and potentiates fibrosis
- PMID: 22013113
- PMCID: PMC3208032
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101288
Binding of anti-SSA antibodies to apoptotic fetal cardiocytes stimulates urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)/uPA receptor-dependent activation of TGF-β and potentiates fibrosis
Abstract
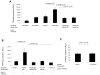
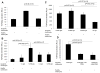
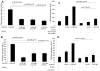
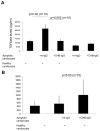
In congenital heart block (CHB), binding of maternal anti-SSA/Ro Abs to fetal apoptotic cardiocytes impairs their removal by healthy cardiocytes and increases urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)/uPA receptor (uPAR)-dependent plasmin activation. Because the uPA/uPAR system plays a role in TGF-β activation, we evaluated whether anti-Ro binding to apoptotic cardiocytes enhances plasmin-mediated activation of TGF-β, thereby promoting a profibrosing phenotype. Supernatants from cocultures of healthy cardiocytes and apoptotic cardiocytes bound by IgG from a mother whose child had CHB (apoptotic-CHB-IgG [apo-CHB-IgG]) exhibited significantly increased levels of active TGF-β compared with supernatants from cocultures of healthy cardiocytes and apoptotic cardiocytes preincubated with IgG from a healthy donor. Treatment of the culture medium with anti-TGF-β Ab or TGF-β inhibitor (SB431542) abrogated the luciferase response, thereby confirming TGF-β dependency. Increased uPA levels and activity were present in supernatants generated from cocultures of healthy cardiocytes and apo-CHB-IgG cardiocytes compared with healthy cardiocytes and apoptotic cardiocytes preincubated with IgG from a healthy donor, respectively. Treatment of apo-CHB-IgG cardiocytes with anti-uPAR or anti-uPA Abs or plasmin inhibitor aprotinin prior to coculturing with healthy cardiocytes attenuated TGF-β activation. Supernatants derived from cocultures of healthy cardiocytes and apo-CHB-IgG cardiocytes promoted Smad2 phosphorylation and fibroblast transdifferentiation, as evidenced by increased smooth muscle actin and collagen expression, which decreased when fibroblasts were treated with supernatants from cocultures pretreated with uPAR Abs. These data suggested that binding of anti-Ro Abs to apoptotic cardiocytes triggers TGF-β activation, by virtue of increasing uPAR-dependent uPA activity, thus initiating and amplifying a cascade of events that promotes myofibroblast transdifferentiation and scar.
Figures

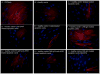

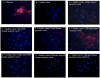
References
-
- Chameides L, et al. Association of maternal systemic lupus erythematosus with congenital complete heart block. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:1204–1207. - PubMed
-
- Frassi M, et al. Neonatal lupus: clinical features and risk of congenital cardiac heart block in newborns from mothers with anti Ro/SSA antibodies. Reumatismo. 2001;53:298–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

