Flagellin, a TLR5 agonist, reduces graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients while enhancing antiviral immunity
- PMID: 22013117
- PMCID: PMC3265143
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101334
Flagellin, a TLR5 agonist, reduces graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients while enhancing antiviral immunity
Abstract
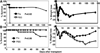
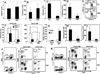
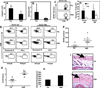
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients treated with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Posttransplant immunosuppressive drugs incompletely control GVHD and increase susceptibility to opportunistic infections. In this study, we used flagellin, a TLR5 agonist protein (∼50 kDa) extracted from bacterial flagella, as a novel experimental treatment strategy to reduce both acute and chronic GVHD in allogeneic HSCT recipients. On the basis of the radioprotective effects of flagellin, we hypothesized that flagellin could ameliorate GVHD in lethally irradiated murine models of allogeneic HSCT. Two doses of highly purified flagellin (administered 3 h before irradiation and 24 h after HSCT) reduced GVHD and led to better survival in both H-2(b) → CB6F1 and H-2(K) → B6 allogeneic HSCT models while preserving >99% donor T cell chimerism. Flagellin treatment preserved long-term posttransplant immune reconstitution characterized by more donor thymic-derived CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells and significantly enhanced antiviral immunity after murine CMV infection. The proliferation index and activation status of donor spleen-derived T cells and serum concentration of proinflammatory cytokines in flagellin-treated recipients were reduced significantly within 4 d posttransplant compared with those of the PBS-treated control recipients. Allogeneic transplantation of radiation chimeras previously engrafted with TLR5 knockout hematopoietic cells showed that interactions between flagellin and TLR5 expressed on both donor hematopoietic and host nonhematopoietic cells were required to reduce GVHD. Thus, the peritransplant administration of flagellin is a novel therapeutic approach to control GVHD while preserving posttransplant donor immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Boiron JM, Lerner D, Pigneux A, Faberes C, Bordessoule D, Turlure P, Cony-Makhoul P, Hau F, Dazey B, Agape P, Reiffers J, Marit G. Allogeneic transplantation for patients with advanced acute leukemia: a single center retrospective study of 92 patients. Leuk Lymphoma. 2001;41:285–296. - PubMed
-
- Dolstra H, Preijers F, Van de Wiel-van Kemenade E, Schattenberg A, Galama J, de Witte T. Expansion of CD8+CD57+ T cells after allogeneic BMT is related with a low incidence of relapse and with cytomegalovirus infection. British journal of haematology. 1995;90:300–307. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara JL, Levy R, Chao NJ. Pathophysiologic mechanisms of acute graft-vs.-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999;5:347–356. - PubMed
-
- Hill GR, Krenger W, Ferrara JL. The role of cytokines in acute graft-versus-host disease. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 1997;3:257–266. - PubMed
-
- Hill GR, Ferrara JL. The primacy of the gastrointestinal tract as a target organ of acute graft-versus-host disease: rationale for the use of cytokine shields in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 2000;95:2754–2759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

