Indirect stimulation of human Vγ2Vδ2 T cells through alterations in isoprenoid metabolism
- PMID: 22013129
- PMCID: PMC3326638
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002697
Indirect stimulation of human Vγ2Vδ2 T cells through alterations in isoprenoid metabolism
Abstract
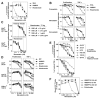
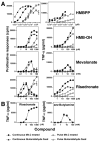
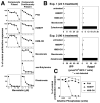
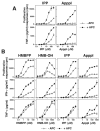
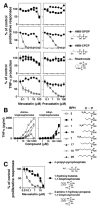
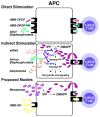
Human Vγ2Vδ2 T cells monitor isoprenoid metabolism by recognizing (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl pyrophosphate (HMBPP), an intermediate in the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway used by microbes, and isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway used by humans. Aminobisphosphonates and alkylamines indirectly stimulate Vγ2Vδ2 cells by inhibiting farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FDPS) in the mevalonate pathway, thereby increasing IPP/triphosphoric acid 1-adenosin-5'-yl ester 3-(3-methylbut-3-enyl) ester that directly stimulate. In this study, we further characterize stimulation by these compounds and define pathways used by new classes of compounds. Consistent with FDPS inhibition, stimulation of Vγ2Vδ2 cells by aminobisphosphonates and alkylamines was much more sensitive to statin inhibition than stimulation by prenyl pyrophosphates; however, the continuous presence of aminobisphosphonates was toxic for T cells and blocked their proliferation. Aminobisphosphonate stimulation was rapid and prolonged, independent of known Ag-presenting molecules, and resistant to fixation. New classes of stimulatory compounds-mevalonate, the alcohol of HMBPP, and alkenyl phosphonates-likely stimulate differently. Mevalonate, a rate-limiting metabolite, appears to enter cells to increase IPP levels, whereas the alcohol of HMBPP and alkenyl phosphonates are directly recognized. The critical chemical feature of bisphosphonates is the amino moiety, because its loss switched aminobisphosphonates to direct Ags. Transfection of APCs with small interfering RNA downregulating FDPS rendered them stimulatory for Vγ2Vδ2 cells and increased cellular IPP. Small interfering RNAs for isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase functioned similarly. Our results show that a variety of manipulations affecting isoprenoid metabolism lead to stimulation of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells and that pulsing aminobisphosphonates would be more effective for the ex vivo expansion of Vγ2Vδ2 T cells for adoptive cancer immunotherapy.
Figures




References
-
- Morita CT, Jin C, Sarikonda G, Wang H. Nonpeptide antigens, presentation mechanisms, and immunological memory of human Vγ2Vδ2 T cells: discriminating friend from foe through the recognition of prenyl pyrophosphate antigens. Immunol Rev. 2007;215:59–76. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm M, Kunzmann V, Eckstein S, Reimer P, Weissinger F, Ruediger T, Tony H-P. γδ T cells for immune therapy of patients with lymphoid malignancies. Blood. 2003;102:200–206. - PubMed
-
- Dieli F, Vermijlen D, Fulfaro F, Caccamo N, Meraviglia S, Cicero G, Roberts A, Buccheri S, D’Asaro M, Gebbia N, Salerno A, Eberl M, Hayday AC. Targeting human γδ T cells with zoledronate and interleukin-2 for immunotherapy of hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:7450–7457. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

