Incidence and human papillomavirus (HPV) type distribution of genital warts in a multinational cohort of men: the HPV in men study
- PMID: 22013227
- PMCID: PMC3209812
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jir652
Incidence and human papillomavirus (HPV) type distribution of genital warts in a multinational cohort of men: the HPV in men study
Abstract
Background: Data on the natural history of human papillomavirus (HPV)-related genital warts (GWs) in men are sparse. We described the distribution of HPV types in incident GWs and estimated GW incidence and time from type-specific incident HPV infections to GW detection in a multinational cohort of men aged 18-70 years.
Methods: Participants included 2487 men examined for GWs and tested for HPV every 6 months and followed up for a median of 17.9 months. Samples were taken from 112 men with incident GWs to test for HPV DNA by polymerase chain reaction.
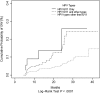
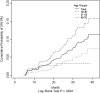
Results: Incidence of GWs was 2.35 cases per 1000 person-years, with highest incidence among men aged 18-30 years (3.43 cases per 1000 person-years). HPV 6 (43.8%), HPV 11 (10.7%), and HPV 16 (9.8%) were the genotypes most commonly detected in GWs. The 24-month cumulative incidence of GWs among men with incident HPV 6/11 infections was 14.6% (95% confidence interval [CI], 7.5%-21.1%). Median time to GW detection was 17.1 months (95% CI, 12.4-19.3 months), with shortest time to detection among men with incident infections with HPV 6/11 only (6.2 months; 95% CI, 5.6-24.2 months).
Conclusions: HPV 6/11 plays an important role in GW development, with the highest incidence and shortest time to detection among men with incident HPV 6/11 infection.
Figures
References
-
- Cates W., Jr. Estimates of the incidence and prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases in the United States. American Social Health Association Panel. Sex Transm Dis. 1999;26:S2–7. - PubMed
-
- Lacey CJ, Lowndes CM, Shah KV. Chapter 4: burden and management of non-cancerous HPV-related conditions: HPV-6/11 disease. Vaccine. 2006;24(Suppl 3):S3/35–41. - PubMed
-
- Dinh TH, Sternberg M, Dunne EF, Markowitz LE. Genital warts among 18- to 59-year-olds in the United States, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2004. Sex Transm Dis. 2008;35:357–60. - PubMed
-
- Koutsky L. Epidemiology of genital human papillomavirus infection. Am J Med. 1997;102:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Jeynes C, Chung MC, Challenor R. ‘Shame on you'—the psychosocial impact of genital warts. Int J STD AIDS. 2009;20:557–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical