Effects of dexmedetomidine added to caudal ropivacaine in paediatric lower abdominal surgeries
- PMID: 22013248
- PMCID: PMC3190506
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5049.84835
Effects of dexmedetomidine added to caudal ropivacaine in paediatric lower abdominal surgeries
Abstract
Purpose: The objectives of this study were to compare the effects of caudal dexmedetomidine combined with ropivacaine to provide postoperative analgesia in children and also to establish its safety in the paediatric population.
Methods: In a randomised, prospective, parallel group, double-blinded study, 60 children were recruited and allocated into two groups: Group RD (n=30) received 0.25% ropivacaine 1 ml/kg with dexmedetomidine 2 μg/kg, making the volume to 0.5 ml and Group R (n=30) received 0.25% ropivacaine 1 ml/kg + 0.5 ml normal saline. Induction of anaesthesia was achieved with 50% N(2)O and 8% sevoflurane in oxygen in spontaneous ventilation. An appropriate-sized LMA was then inserted and a caudal block performed in all patients. Behaviour during emergence was rated with a 4-point scale, sedation with Ramsay's sedation scale, and pain assessed with face, legs, activity, cry, consolability (FLACC) pain score.
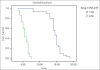
Results: The duration of postoperative analgesia recorded a median of 5.5 hours in Group R compared with 14.5 hours in Group RD, with a P value of <0.001. Group R patients achieved a statistically significant higher FLACC score compared with Group RD patients. The difference between the means of mean sedation score, emergence behaviour score, mean emergence time was statistically highly significant (P<0.001). The peri-operative haemodynamics were stable among both the groups.
Conclusion: Caudal dexmedetomidine (2 μg/kg) with 0.25% ropivacaine (1 ml/kg) for paediatric lower abdominal surgeries achieved significant postoperative pain relief that resulted in a better quality of sleep and a prolonged duration of arousable sedation and produced less incidence of emergence agitation following sevoflurane anaesthesia.
Keywords: Analgesia; anaesthesia; caudal; dexmedetomidine; emergence agitation; postoperative period; ropivacaine; sevoflurane.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Deng XM, Xiao WJ, Tang GZ, Luo MP, Xu KL. The minimum local anesthetic concentration of ropivacaine for caudal analgesia in children. Anesth Analg. 2002;94:1465–8. - PubMed
-
- Birbicer H, Doruk N, Cinel I, Atici S, Avlan D, Bilgin E, et al. Could adding magnesium as adjuvant to ropivacaine in caudal anaesthesia improve postoperative pain control. Pediatr Surg Int. 2007;23:195–8. - PubMed
-
- Ray M, Mondal SK, Biswas A. Caudal analgesia in paediatric patients: Comparison between Bupivacaine and Ropivacaine. Indian J Anaesth. 2003;47:275–8.
-
- El-Hennawy AM, Abd-Elwahab AM, Abd-Elmaksoud AM, El-Ozairy HS, Boulis SR. Addition of clonidine or dexmedetomidine to bupivacaine prolongs caudal analgesia in children. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103:268–74. - PubMed
-
- Ibacache M, Muñoz H, Brandes V. Single-dose dexmedetomidine reduces agitation after sevoflurane anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2004;98:60–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

