Novel positron emission tomography radiotracers in brain tumor imaging
- PMID: 22013296
- PMCID: PMC3190493
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-3026.85369
Novel positron emission tomography radiotracers in brain tumor imaging
Abstract
Although [18F] 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG) is the most widely used radiopharmaceutical the world over, it is not the ideal tracer for brain imaging, owing to its high physiological cortical uptake and lack of specificity. This has paved the way for the introduction of several novel radiotracers, each with their own inherent strengths and limitations. We present the insights gained from the use of these radiotracers at our institution.
Keywords: Brain tumor; Novel Positron emission tomography radiotracers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
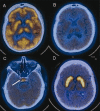
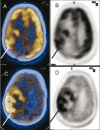
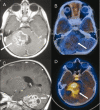
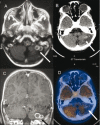
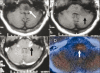
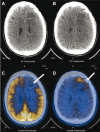

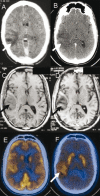
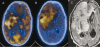
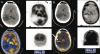
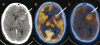
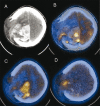
References
-
- Patronas NJ, Chiro G, Brooks RA, DeLaPaz RL, Kornblith PL, Smith BH, et al. Work in progress: [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography in the evaluation of radiation necrosis of the brain. Radiology. 1982;144:885–9. - PubMed
-
- Kracht LW, Miletic H, Busch S, Jacobs AH, Voges J, Hoevels M, et al. Delineation of brain tumor extent with [11C]L-methionine positron emission tomography: Local comparison with stereotactic histopathology. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:7163–71. - PubMed
-
- Jager PL, Vaalburg W, Pruim J, Vries EG, Langen KJ, Piers DA. Radiolabeled amino acids: Basic aspects and clinical applications in oncology. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:432–45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

