Diffusion tensor imaging in spinal cord injury
- PMID: 22013299
- PMCID: PMC3190496
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-3026.85372
Diffusion tensor imaging in spinal cord injury
Abstract
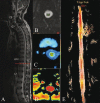
Background and purpose: To assess the feasibility of spinal tractography in patients of spinal cord injury vs a control group and to compare fractional anisotropy (FA) values between the groups.
Materials and methods: Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was performed in the spinal cord of 29 patients (18 patients and 11 controls). DTI was done in the cervical region if the cord injury was at the dorsal or lumbar region and in the conus region if cord injury was in the cervical or dorsal region. FA was calculated for the patients and the controls and the values were compared.
Results: The mean FA value was 0.550±0.09 in the control group and 0.367±0.14 in the patients; this difference was statistically significant (P=0.001).
Conclusion: Spinal tractography is a feasible technique to assess the extent of spinal cord injury by FA, which is reduced in patients of spinal cord injury, suggesting possible Wallerian degeneration. In future, this technique may become a useful tool for assessing cord injury patients after stem cell therapy, with improvement in FA values indicating axonal regeneration.
Keywords: Fractional anisotropy; MRI; spinal cord injury; tensor imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lin VW, Cardenas DD, Cutter NC, Frost FS, Hammond MC. New York: Demos Medical Publishing; 2002. Spinal Cord Medicine: Principles and Practice.
-
- Inglese M, Makani S, Johnson G, Cohen BA, Silver JA, Gonen O, et al. Diffuse axonal injury in mild traumatic brain injury: A diffusion tensor imaging study. J Neurosurg. 2005;103:298–303. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

