Optimization of nonlinear dose- and concentration-response models utilizing evolutionary computation
- PMID: 22013401
- PMCID: PMC3186933
- DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.09-030.Beam
Optimization of nonlinear dose- and concentration-response models utilizing evolutionary computation
Abstract
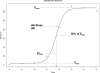
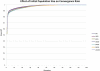
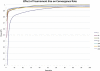
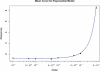
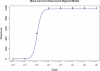
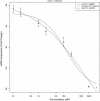
An essential part of toxicity and chemical screening is assessing the concentrated related effects of a test article. Most often this concentration-response is a nonlinear, necessitating sophisticated regression methodologies. The parameters derived from curve fitting are essential in determining a test article's potency (EC(50)) and efficacy (E(max)) and variations in model fit may lead to different conclusions about an article's performance and safety. Previous approaches have leveraged advanced statistical and mathematical techniques to implement nonlinear least squares (NLS) for obtaining the parameters defining such a curve. These approaches, while mathematically rigorous, suffer from initial value sensitivity, computational intensity, and rely on complex and intricate computational and numerical techniques. However if there is a known mathematical model that can reliably predict the data, then nonlinear regression may be equally viewed as parameter optimization. In this context, one may utilize proven techniques from machine learning, such as evolutionary algorithms, which are robust, powerful, and require far less computational framework to optimize the defining parameters. In the current study we present a new method that uses such techniques, Evolutionary Algorithm Dose Response Modeling (EADRM), and demonstrate its effectiveness compared to more conventional methods on both real and simulated data.
Keywords: Evolutionary Algorithm; Hill-Slope Model; Nonlinear Regression; Parameter Estimation.
Figures






References
-
- Bates DM, Watts DG. Nonlinear Regression, Analysis and its Applications. John Wiley; New York: 1988.
-
- Björck A. Numerical methods for least squares problems. SIAM; Philadelphia: 1996.
-
- Chamjangali MA, Beglari M, Bagherian G. Prediction of cytotoxicity data (CC50) of anti-HIV 5-pheny-l-phenylamino-1H-imidazole derivatives by artificial neural network trained with Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm. J of Molecular Graphics and Modelling. 2007;26(1):360–367. - PubMed
-
- Delahaye D, Puechmorel S. Air Traffic Controller Keyboard Optimization by Artificial Evolution. Lect Not Comp Sci. 2004;2936:177–188.
-
- Dennis JE, Gay DM, Welsch RE. Algorithm 573. NL2SOL — An adaptive nonlinear least-squares algorithm, ACM Trans. Math. Software. 1981;7:369–383.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

