RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT Signaling in Malignant Melanoma Progression and Therapy
- PMID: 22013435
- PMCID: PMC3195305
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/354191
RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT Signaling in Malignant Melanoma Progression and Therapy
Abstract
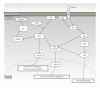
Cutaneous malignant melanoma is one of the most serious skin cancers and is highly invasive and markedly resistant to conventional therapy. Melanomagenesis is initially triggered by environmental agents including ultraviolet (UV), which induces genetic/epigenetic alterations in the chromosomes of melanocytes. In human melanomas, the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK (MAPK) and the PI3K/PTEN/AKT (AKT) signaling pathways are two major signaling pathways and are constitutively activated through genetic alterations. Mutations of RAF, RAS, and PTEN contribute to antiapoptosis, abnormal proliferation, angiogenesis, and invasion for melanoma development and progression. To find better approaches to therapies for patients, understanding these MAPK and AKT signaling mechanisms of melanoma development and progression is important. Here, we review MAPK and AKT signaling networks associated with melanoma development and progression.
Figures
References
-
- Kato M, Hattori T, Ito H, et al. Serum-soluble Fas levels as a marker to distinguish allergic and nonallergic rhinitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1999;103(6):1213–1214. - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Kato M, Akhand AA, et al. 4-hydroxynonenal induces a cellular redox status-related activation of the caspase cascade for apoptotic cell death. Journal of Cell Science. 2000;113, part 4:635–641. - PubMed
-
- Kato M, Takeda K, Kawamoto Y, et al. Repair by Src kinase of function-impaired RET with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A mutation with substitutions of tyrosines in the COOH-terminal kinase domain for phenylalanine. Cancer Research. 2002;62(8):2414–2422. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

