Resveratrol regulates antioxidant status, inhibits cytokine expression and restricts apoptosis in carbon tetrachloride induced rat hepatic injury
- PMID: 22013498
- PMCID: PMC3195554
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/703676
Resveratrol regulates antioxidant status, inhibits cytokine expression and restricts apoptosis in carbon tetrachloride induced rat hepatic injury
Abstract
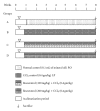
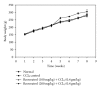
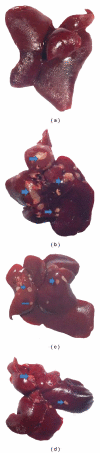
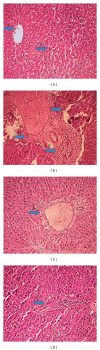
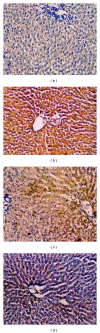
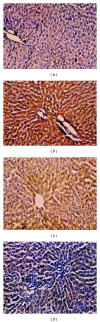
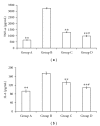
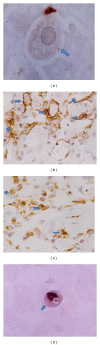
Recent studies indicate the chemopreventive role of resveratrol in many animal models like ischemia, rheumatoid arthritis, human cancer, and diabetes. The present study was designed to investigate the chemopreventive potential of resveratrol in rat hepatic injury model by carbon tetrachloride. Male Wistar rats were treated with carbon tetrachloride (0.4 g/kg body weight) intraperitoneally daily for 8 weeks. Resveratrol (100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg body weight) was given orally from first day until the last day of experiment. The investigation assesses the effect of resveratrol on morphological, oxidative status, histopathological, immunohistochemical, and apoptotic analysis in carbon tetrachloride-challenged liver tissue. The study indicated that the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 were profoundly expressed in experimental rats, whereas resveratrol decreases the immunopositivity of TNF-α and IL-6 and restored the altered architectural structure of challenged hepatic tissue. Resveratrol also protects liver cells by suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combination of metformin and luteolin synergistically protects carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity: Mechanism involves antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Biofactors. 2019 Jul;45(4):598-606. doi: 10.1002/biof.1521. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Biofactors. 2019. PMID: 31336028
-
Resveratrol attenuates cyclophosphamide-induced hepatic apoptosis in association with the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation in a rat model of acute liver injury.Tissue Cell. 2025 Apr;93:102728. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2025.102728. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Tissue Cell. 2025. PMID: 39808867
-
Resveratrol can prevent CCl₄-induced liver injury by inhibiting Notch signaling pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2016 Jul;31(7):769-84. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-720. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Histol Histopathol. 2016. PMID: 26742567
-
Resveratrol ameliorates hepatic injury via the mitochondrial pathway in rats with severe acute pancreatitis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 28;601(1-3):136-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.10.017. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18977215
-
Meloxicam modulates oxidative stress status, inhibits prostaglandin E2, and abrogates apoptosis in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat hepatic injury.Int J Toxicol. 2012 Jun;31(3):276-86. doi: 10.1177/1091581812442939. Epub 2012 May 3. Int J Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22556387
Cited by
-
Critical review of resveratrol in xenobiotic-induced hepatotoxicity.Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Dec;86:309-18. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26561740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol treatment ameliorates hepatic damage via the TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway in a phenobarbital/CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(9):1124-1133. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.75737.16398. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39055873 Free PMC article.
-
The antimetastatic effects of resveratrol on hepatocellular carcinoma through the downregulation of a metastasis-associated protease by SP-1 modulation.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056661. Epub 2013 Feb 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437203 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: a promising intervention for control of carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 May 3;15:142. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0655-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 25935744 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol and liver: A systematic review.J Res Med Sci. 2015 Aug;20(8):797-810. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.168405. J Res Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26664429 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu D, Zhai Q, Shi X. Alcohol-induced oxidative stress and cell responses. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2006;21(3):S26–S29. - PubMed
-
- Loguercio C, Federico A. Oxidative stress in viral and alcoholic hepatitis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2003;34(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Benzie IF. Evolution of antioxidant defence mechanisms. European Journal of Nutrition. 2000;39(2):53–61. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Gores GJ, Cederbaum AI, Hinson JA, Pessayre D, Lemasters JJ. Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity. Toxicological Sciences. 2002;65(2):166–176. - PubMed
-
- Plaa GL, Charbonneau M. Detection and evaluation of chemically induced liver injury. In: Hayes W, editor. Principles and Methods of Toxicology. New York, NY, USA: Raven Press; 2001. pp. 1145–1178.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

