A ssDNA Aptamer That Blocks the Function of the Anti-FLAG M2 Antibody
- PMID: 22013507
- PMCID: PMC3195435
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/720798
A ssDNA Aptamer That Blocks the Function of the Anti-FLAG M2 Antibody
Abstract
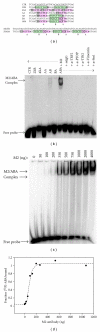
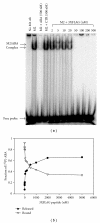
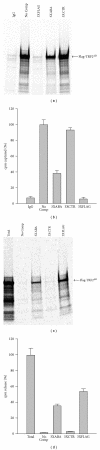
Using SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment), we serendipitously discovered a ssDNA aptamer that binds selectively to the anti-FLAG M2 antibody. The aptamer consisted of two motifs (CCTTA and TGTCTWCC) separated by 2-3 bases, and the elimination of one or the other motif abrogated binding. The DNA aptamer and FLAG peptide competed for binding to the antigen-binding pocket of the M2 antibody. In addition, the aptamer eluted FLAG-tagged proteins from the antibody, suggesting a commercial application in protein purification. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of using SELEX to develop ssDNA aptamers that block the function of a specific antibody, a capability that could lead to the development of novel therapeutic modalities for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Lyons R, Narain S, Nichols C, Satoh M, Reeves WH. Effective use of autoantibody tests in the diagnosis of systemic autoimmune disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2005;1050:217–228. - PubMed
-
- Pisetsky DS, Caster SA. Binding specificity of a monoclonal anti-DNA antibody. Molecular Immunology. 1982;19(5):645–650. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki T, Muryoi T, Sekiguchi Y, Tamate E, Yoshinaga K, Kitagawa Y. Monoclonal human anti-DNA antibodies from EB virus-transformed lymphocytes of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Journal of Clinical Immunology. 1985;5(4):246–253. - PubMed
-
- DeGiorgio LA, Konstantinov KN, Lee SC, Hardin JA, Volpe BT, Diamond B. A subset of lupus anti-DNA antibodies cross-reacts with the NR2 glutamate receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature Medicine. 2001;7(11):1189–1193. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

