Autoradiographic Mapping of 5-HT(1B/1D) Binding Sites in the Rhesus Monkey Brain Using [carbonyl-C]zolmitriptan
- PMID: 22013519
- PMCID: PMC3195497
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/694179
Autoradiographic Mapping of 5-HT(1B/1D) Binding Sites in the Rhesus Monkey Brain Using [carbonyl-C]zolmitriptan
Abstract
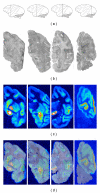
Zolmitriptan is a serotonin 5-HT(1B/1D) receptor agonist that is an effective and well-tolerated drug for migraine treatment. In a human positron emission tomography study, [(11)C]zolmitriptan crossed the blood-brain barrier but no clear pattern of regional uptake was discernable. The objective of this study was to map the binding of [(11)C]zolmitriptan in Rhesus monkey brain using whole hemisphere in vitro autoradiography with [(11)C]zolmitriptan as a radioligand. In saturation studies, [(11)C]zolmitriptan showed specific (90%) binding to a population of high-affinity binding sites (Kd 0.95-5.06 nM). There was regional distribution of binding sites with the highest density in the ventral pallidum, followed by the external globus pallidus, substantia nigra, visual cortex, and nucleus accumbens. In competitive binding studies with 5-HT(1) receptor antagonists, [(11)C]zolmitriptan binding was blocked by selective 5-HT(1B) and 5-HT(1D) ligands in all target areas. There was no appreciable change in binding with the addition of a 5-HT(1A) receptor antagonist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Autoradiographic mapping of 5-HT(1B) and 5-HT(1D) receptors in the post mortem human brain using [(3)H]GR 125743.Brain Res. 2001 Oct 5;915(1):47-57. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02823-2. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11578619
-
Serotonergic effects and extracellular brain levels of eletriptan, zolmitriptan and sumatriptan in rat brain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Aug 17;425(3):203-10. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01151-7. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11513839
-
A comparative autoradiographic study of 5-HT1D binding sites in human and guinea-pig brain using different radioligands.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Jan;21(1-2):19-29. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90374-3. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994. PMID: 8164519
-
Serotonin receptors in brain revisited.Brain Res. 2016 Aug 15;1645:46-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.042. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26740406 Review.
-
5-HT 1B/D receptor antagonists.Gen Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;29(3):293-303. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(96)00460-0. Gen Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9378233 Review.
Cited by
-
[11C]Carbon monoxide: advances in production and application to PET radiotracer development over the past 15 years.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2019 Sep 18;4(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s41181-019-0073-4. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2019. PMID: 31659516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"In-loop" carbonylation-A simplified method for carbon-11 labelling of drugs and radioligands.J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2020 Mar;63(3):100-107. doi: 10.1002/jlcr.3805. Epub 2020 Jan 21. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2020. PMID: 31524295 Free PMC article.
-
(11)C[double bond, length as m-dash]O bonds made easily for positron emission tomography radiopharmaceuticals.Chem Soc Rev. 2016 Aug 22;45(17):4708-26. doi: 10.1039/c6cs00310a. Chem Soc Rev. 2016. PMID: 27276357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goadsby PJ. The pharmacology of headache. Progress in Neurobiology. 2000;62(5):509–525. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L. Peripheral and central trigeminovascular activation in cat is blocked by the serotonin (5HT)-1D receptor agonist 311C90. Headache. 1994;34(7):394–399. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ, Hoskin KL. Inhibition of trigeminal neurons by intravenous administration of the serotonin (5HT)(1B/D) receptor agonist zolmitriptan (311C90): are brain stem sites therapeutic target in migraine? Pain. 1996;67(2-3):355–359. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ, Knight YE. Direct evidence for central sites of action of zolmitriptan (311C90): an autoradiographic study in cat. Cephalalgia. 1997;17(3):153–158. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

