Combination therapy of renal cell carcinoma or breast cancer patients with dendritic cell vaccine and IL-2: results from a phase I/II trial
- PMID: 22013914
- PMCID: PMC3213212
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-178
Combination therapy of renal cell carcinoma or breast cancer patients with dendritic cell vaccine and IL-2: results from a phase I/II trial
Abstract
Background: Ten cancer patients (Six renal cell carcinoma and four breast cancer patients) were treated in a phase I/II study with a vaccine composed of autologous dendritic cells (DCs) and IL-2 to evaluate the DC vaccine-related toxicity and antigen-specific immune alteration.
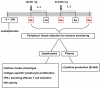
Methods: Cancer patients were treated twice with autologous CD34+ hematopoietic stem cell-derived, GM-CSF/IFN-γ-differentiated DCs pulsed with autologous tumor lysate and KLH, by 4-week interval. Following each subcutaneous injection of therapeutic DCs, low-dose (200 MIU) IL-2 was introduced for 14 consecutive days as an immune adjuvant. To determine the DC vaccine-induced immunological alterations, the KLH-specific lymphocyte proliferation, number of IFN-γ secreting T cells (ELISPOT assay), NK activity and the cytokine modulation were measured.
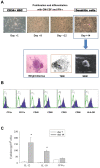
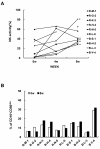
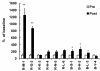
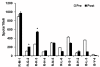
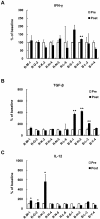
Results: Cultured-DCs expressing HLA-DR, CD11c, CD83, and B7.1/B7.2 produced IL-12p70. After vaccination, the patients tolerated it. Clinical response was observed in one RCC patient as stable disease. However DC-vaccine related antigen-specific immune responses including peripheral blood lymphocyte proliferation and the number of IFN-r secreting cells were induced in six patients without clear correlation with clinical responses. Also NK activity was induced significantly in six patients after vaccination. DC vaccine-related decrease of TGF-β level or increase of IL-12p70 level and decline of CD4+CD25+ T cells were observed in three patients. However only in the RCC patient whose disease stabilized, combination of stimulatory as well as inhibitory immune alterations including induction of IFN-γ secreting T cell with reduction of CD4+ CD25+ T cell were correlated with clinical responses.
Conclusion: Data indicated that DC vaccine combined with IL-2 is well tolerated without major side effects. DC vaccine induced the specific immunity against introduced antigen. Combinatorial alterations of immunological parameters indicating antigen-specific immune induction along with reduction of inhibitory immunity were correlated with clinical responses in DC vaccine treated patients.
Figures
References
-
- Fernandez NC, Flament C, Crepineau F. et al.Dendritic cells (DC) promote natural killer (NK) cell functions: dynamics of the human DC/NK cell cross talk. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2002;13:17–27. - PubMed
-
- Mailliard RB, Son YI, Redlinger R. et al.Dendritic cells mediate NK cell help for Th1 and CTL responses: two-signal requirement for the induction of NK cell helper function. J Immunol. 2003;171:2366–2373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

