Hospitalizations due to rotavirus gastroenteritis in Catalonia, Spain, 2003-2008
- PMID: 22013948
- PMCID: PMC3212997
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-429
Hospitalizations due to rotavirus gastroenteritis in Catalonia, Spain, 2003-2008
Abstract
Background: Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe gastroenteritis among young children in Spain and worldwide. We evaluated hospitalizations due to community and hospital-acquired rotavirus gastroenteritis (RVGE) and estimated related costs in children under 5 years old in Catalonia, Spain.
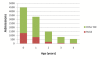
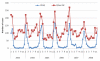
Results: We analyzed hospital discharge data from the Catalan Health Services regarding hospital admissions coded as infectious gastroenteritis in children under 5 for the period 2003-2008. In order to estimate admission incidence, we used population estimates for each study year published by the Statistic Institut of Catalonia (Idescat). The costs associated with hospital admissions due to rotavirus diarrhea were estimated for the same years. A decision tree model was used to estimate the threshold cost of rotavirus vaccine to achieve cost savings from the healthcare system perspective in Catalonia. From 2003 through 2008, 10655 children under 5 years old were admitted with infectious gastroenteritis (IGE). Twenty-two percent of these admissions were coded as RVGE, yielding an estimated average annual incidence of 104 RVGE hospitalizations per 100000 children in Catalonia. Eighty seven percent of admissions for RVGE occurred during December through March. The mean hospital stay was 3.7 days, 0.6 days longer than for other IGE. An additional 892 cases of presumed nosocomial RVGE were detected, yielding an incidence of 2.5 cases per 1000 child admissions. Total rotavirus hospitalization costs due to community acquired RVGE for the years 2003 and 2008 were 431,593 and 809,224 €, respectively. According to the estimated incidence and hospitalization costs, immunization would result in health system cost savings if the cost of the vaccine was 1.93 € or less. At a vaccine cost of 187 € the incremental cost per hospitalization prevented is 195,388 € (CI 95% 159,300; 238,400).
Conclusions: The burden of hospitalizations attributable to rotavirus appeared to be lower in Catalonia than in other regions of Spain and Europe. The relatively low incidence of hospitalization due to rotavirus makes rotavirus vaccination less cost-effective in Catalonia than in other areas with higher rotavirus disease burden.
Figures

References
-
- Parashar UD, Burton A, Lanata C, Boschi-Pinto C, Shibuya K, Steele D, Birmingham M, Glass RI. Global mortality associated with rotavirus disease among children in 2004. J Infect Dis. 2009;200(Suppl 1):9–15. - PubMed
-
- Soriano-Gabarro M, Mrukowicz J, Vesikari T, Verstraeten T. Burden of rotavirus disease in European Union countries. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25(Suppl 1):7–11. - PubMed
-
- Rheingans RD, Heylen J, Giaquinto C. Economics of rotavirus gastroenteritis and vaccination in Europe: what makes sense? Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006;25(Suppl 1):48–55. - PubMed

