OATPs, OATs and OCTs: the organic anion and cation transporters of the SLCO and SLC22A gene superfamilies
- PMID: 22013971
- PMCID: PMC3372714
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01724.x
OATPs, OATs and OCTs: the organic anion and cation transporters of the SLCO and SLC22A gene superfamilies
Abstract
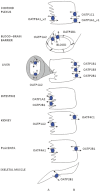
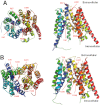
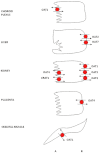
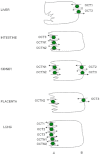
The human organic anion and cation transporters are classified within two SLC superfamilies. Superfamily SLCO (formerly SLC21A) consists of organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs), while the organic anion transporters (OATs) and the organic cation transporters (OCTs) are classified in the SLC22A superfamily. Individual members of each superfamily are expressed in essentially every epithelium throughout the body, where they play a significant role in drug absorption, distribution and elimination. Substrates of OATPs are mainly large hydrophobic organic anions, while OATs transport smaller and more hydrophilic organic anions and OCTs transport organic cations. In addition to endogenous substrates, such as steroids, hormones and neurotransmitters, numerous drugs and other xenobiotics are transported by these proteins, including statins, antivirals, antibiotics and anticancer drugs. Expression of OATPs, OATs and OCTs can be regulated at the protein or transcriptional level and appears to vary within each family by both protein and tissue type. All three superfamilies consist of 12 transmembrane domain proteins that have intracellular termini. Although no crystal structures have yet been determined, combinations of homology modelling and mutation experiments have been used to explore the mechanism of substrate recognition and transport. Several polymorphisms identified in members of these superfamilies have been shown to affect pharmacokinetics of their drug substrates, confirming the importance of these drug transporters for efficient pharmacological therapy. This review, unlike other reviews that focus on a single transporter family, briefly summarizes the current knowledge of all the functionally characterized human organic anion and cation drug uptake transporters of the SLCO and the SLC22A superfamilies.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SLC Family Transporters.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1141:101-202. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-7647-4_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31571165 Review.
-
Overview of organic anion transporters and organic anion transporter polypeptides and their roles in the liver.World J Clin Cases. 2019 Dec 6;7(23):3915-3933. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3915. World J Clin Cases. 2019. PMID: 31832394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug uptake systems in liver and kidney.Curr Drug Metab. 2003 Jun;4(3):185-211. doi: 10.2174/1389200033489460. Curr Drug Metab. 2003. PMID: 12769665 Review.
-
Organic anion transporting polypeptides: Pharmacology, toxicology, structure, and transport mechanisms.Pharmacol Rev. 2025 Mar;77(2):100023. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmr.2024.100023. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Pharmacol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40148036 Review.
-
Trafficking and other regulatory mechanisms for organic anion transporting polypeptides and organic anion transporters that modulate cellular drug and xenobiotic influx and that are dysregulated in disease.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;174(13):1908-1924. doi: 10.1111/bph.13785. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28299773 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular prostaglandin E2 contributes to hypoxia-induced proximal tubular cell death.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 29;11(1):7047. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86219-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33782420 Free PMC article.
-
Low oxygen tension differentially regulates the expression of placental solute carriers and ABC transporters.FEBS Lett. 2021 Mar;595(6):811-827. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13937. Epub 2020 Oct 7. FEBS Lett. 2021. PMID: 32978975 Free PMC article.
-
Drug interactions of meglitinide antidiabetics involving CYP enzymes and OATP1B1 transporter.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Apr 6;9(8):259-268. doi: 10.1177/2042018818767220. eCollection 2018. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30181852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transporter and Lysosomal Mediated (Multi)drug Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Potential Strategies to Overcome Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Dec 10;10(12):503. doi: 10.3390/cancers10120503. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30544701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of p53 on Aristolochic Acid I-Induced Gene Expression In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 6;20(24):6155. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246155. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31817608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe T, Kakyo M, Tokui T, Nakagomi R, Nishio T, Nakai D, et al. Identification of a novel gene family encoding human liver-specific organic anion transporter LST-1. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17159–17163. - PubMed
-
- Abe T, Unno M, Onogawa T, Tokui T, Kondo TN, Nakagomi R, et al. LST-2, a human liver-specific organic anion transporter, determines methotrexate sensitivity in gastrointestinal cancers. Gastroenterology. 2001;120:1689–1699. - PubMed
-
- Adachi H, Suzuki T, Abe M, Asano N, Mizutamari H, Tanemoto M, et al. Molecular characterization of human and rat organic anion transporter OATP-D. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;285:F1188–F1197. - PubMed
-
- Aherne W, Piall E, Marks V. Radioimmunoassay of methotrexate: use of 75Se-labelled methotrexate. Ann Clin Biochem. 1978b;15:331–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

