Pu-Erh tea and GABA attenuates oxidative stress in kainic acid-induced status epilepticus
- PMID: 22014163
- PMCID: PMC3217899
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-18-75
Pu-Erh tea and GABA attenuates oxidative stress in kainic acid-induced status epilepticus
Abstract
Background: Pu-Erh tea is one of the most-consumed beverages due to its taste and the anti-anxiety-producing effect of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) if contains. However the protective effects of Pu-Erh tea and its constituent, GABA to kainic acid (KA)-induced seizure have not been fully investigated.
Methods: We analyzed the effect of Pu-Erh tea leaf (PETL) and GABA on KA-induced neuronal injury in vivo and in vitro.
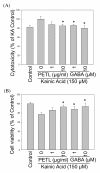
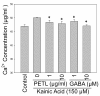
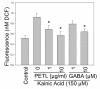
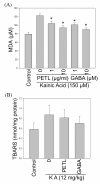
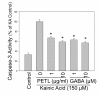
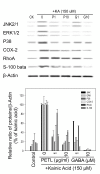
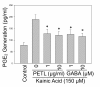
Results: PETL and GABA reduced the maximal seizure classes, predominant behavioral seizure patterns, and lipid peroxidation in male FVB mice with status epilepticus. PETL extracts and GABA were effective in protecting KA-treated PC12 cells in a dose-dependent manner and they decreased Ca(2+) release, ROS production and lipid peroxidation from KA-stressed PC12 cells. Western blot results revealed that mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), RhoA and cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression were increased in PC12 cells under KA stress, and PETL and GABA significantly reduced COX-2 and p38 MAPK expression, but not that of RhoA. Furthermore, PETL and GABA reduced PGE(2) production from KA-induced PC12 cells.
Conclusions: Taken together, PETL and GABA have neuroprotective effects against excitotoxins that may have clinical applications in epilepsy.
Figures

References
-
- Chiang CT, Weng MS, Lin-Shiau SY, Kuo KL, Tsai YJ, Lin JK. Pu-erh tea supplementation suppresses fatty acid synthase expression in the rat liver through downregulating Akt and JNK signalings as demonstrated in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Oncol Res. 2005;16:119–128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

