Role of neurosteroids in the anticonvulsant activity of midazolam
- PMID: 22014182
- PMCID: PMC3423249
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01733.x
Role of neurosteroids in the anticonvulsant activity of midazolam
Abstract
Background and purpose: Midazolam is a short-acting benzodiazepine that is widely used as an i.v. sedative and anticonvulsant. Besides interacting with the benzodiazepine site associated with GABA(A) receptors, some benzodiazepines act as agonists of translocator protein (18 kDa) (TSPO) to enhance the synthesis of steroids, including neurosteroids with positive modulatory actions on GABA(A) receptors. We sought to determine if neurosteroidogenesis induced by midazolam contributes to its anticonvulsant action.
Experimental approach: Mice were pretreated with neurosteroid synthesis inhibitors and potentiators followed by midazolam or clonazepam, a weak TSPO ligand. Anticonvulsant activity was assessed with the i.v. pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) threshold test.
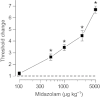
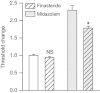
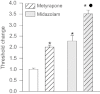
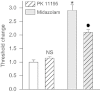
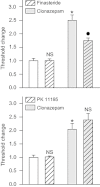
Key results: Midazolam (500-5000 µg·kg(-1) , i.p.) caused a dose-dependent increase in seizure threshold. Pretreatment with the neurosteroid synthesis inhibitors finasteride, a 5α-reductase inhibitor, and a functional TSPO antagonist PK 11195, reduced the anticonvulsant action of midazolam. The anticonvulsant action of midazolam was enhanced by the neurosteroidogenic drug metyrapone, an 11β-hydroxylase inhibitor. In contrast, the anticonvulsant action of clonazepam (100 µg·kg(-1) ) was reduced by finasteride but not by PK 11195, indicating a possible contribution of neurosteroids unrelated to TSPO.
Conclusion and implications: Enhanced endogenous neurosteroid synthesis, possibly mediated by an interaction with TSPO, contributed to the anticonvulsant action of midazolam. Enhanced neurosteroidogenesis may also be a factor in the actions of other benzodiazepines, even those that only weakly interact with TSPO.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Akula KK, Dhir A, Kulkarni SK. Effect of various antiepileptic drugs in a pentylenetetrazol-induced seizure model in mice. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2009;31:423–432. - PubMed
-
- Auta J, Romeo E, Kozikowski A, Ma D, Costa E, Guidotti A. Participation of mitochondrial diazepam binding inhibitor receptors in the anticonflict, antineophobic and anticonvulsant action of 2-aryl-3-indoleacetamide and imidazopyridine derivatives. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:649–656. - PubMed
-
- Bender AS, Hertz L. Pharmacological characteristics of diazepam receptors in neurons and astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18:366–372. - PubMed
-
- Bitran D, Foley M, Audette D, Leslie N, Frye CA. Activation of peripheral mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors in the hippocampus stimulates allopregnanolone synthesis and produces anxiolytic-like effects in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;151:64–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

