Involvement of the beta-endorphin neurons of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in ethanol-induced place preference conditioning in mice
- PMID: 22014186
- PMCID: PMC4151392
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01553.x
Involvement of the beta-endorphin neurons of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in ethanol-induced place preference conditioning in mice
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence indicates that mu- and delta-opioid receptors are decisively involved in the retrieval of memories underlying conditioned effects of ethanol. The precise mechanism by which these receptors participate in such effects remains unclear. Given the important role of the proopiomelanocortin (POMc)-derived opioid peptide beta-endorphin, an endogenous mu- and delta-opioid receptor agonist, in some of the behavioral effects of ethanol, we hypothesized that beta-endorphin would also be involved in ethanol conditioning.
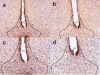
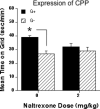
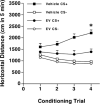
Methods: In this study, we treated female Swiss mice with estradiol valerate (EV), which induces a neurotoxic lesion of the beta-endorphin neurons of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ArcN). These mice were compared to saline-treated controls to investigate the role of beta-endorphin in the acquisition, extinction, and reinstatement of ethanol (0 or 2 g/kg; intraperitoneally)-induced conditioned place preference (CPP).
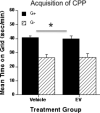
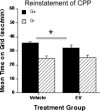
Results: Immunohistochemical analyses confirmed a decreased number of POMc-containing neurons of the ArcN with EV treatment. EV did not affect the acquisition or reinstatement of ethanol-induced CPP, but facilitated its extinction. Behavioral sensitization to ethanol, seen during the conditioning days, was not present in EV-treated animals.
Conclusions: The present data suggest that ArcN beta-endorphins are involved in the retrieval of conditioned memories of ethanol and are implicated in the processes that underlie extinction of ethanol-cue associations. Results also reveal a dissociated neurobiology supporting behavioral sensitization to ethanol and its conditioning properties, as a beta-endorphin deficit affected sensitization to ethanol, while leaving acquisition and reinstatement of ethanol-induced CPP unaffected.
Copyright © 2011 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures
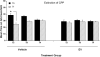
References
-
- Allen SA, Grisel JE. Absence of EtOH-induced sensitization in b-endorphin deficient mice. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2005;29:P824.
-
- Angelogianni P, Gianoulakis C. Prenatal exposure to ethanol alters the ontogeny of the beta-endorphin response to stress. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1989;13:564–571. - PubMed
-
- Bahar A, Samuel A, Hazvi S, Dudai Y. The amygdalar circuit that acquires taste aversion memory differs from the circuit that extinguishes it. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2003;17:1527–1530. - PubMed
-
- Bardo MT, Bevins RA. Conditioned place preference: what does it add to our preclinical understanding of drug reward? Psychopharmacology. 2000;153:31–43. - PubMed
-
- Barros DM, Izquierdo LA, Medina JH, Izquierdo I. Pharmacological findings contribute to the understanding of the main physiological mechanisms of memory retrieval. Current Drug Targets CNS and Neurological Disorders. 2003;2:81–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

