Activated MCTC mast cells infiltrate diseased lung areas in cystic fibrosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 22014187
- PMCID: PMC3209449
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-139
Activated MCTC mast cells infiltrate diseased lung areas in cystic fibrosis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Although mast cells are regarded as important regulators of inflammation and tissue remodelling, their role in cystic fibrosis (CF) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) has remained less studied. This study investigates the densities and phenotypes of mast cell populations in multiple lung compartments from patients with CF, IPF and never smoking controls.
Methods: Small airways, pulmonary vessels, and lung parenchyma were subjected to detailed immunohistochemical analyses using lungs from patients with CF (20 lung regions; 5 patients), IPF (21 regions; 7 patients) and controls (16 regions; 8 subjects). In each compartment the densities and distribution of MCT and MCTC mast cell populations were studied as well as the mast cell expression of IL-6 and TGF-β.
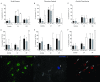
Results: In the alveolar parenchyma in lungs from patients with CF, MCTC numbers increased in areas showing cellular inflammation or fibrosis compared to controls. Apart from an altered balance between MCTC and MCT cells, mast cell in CF lungs showed elevated expression of IL-6. In CF, a decrease in total mast cell numbers was observed in small airways and pulmonary vessels. In patients with IPF, a significantly elevated MCTC density was present in fibrotic areas of the alveolar parenchyma with increased mast cell expression of TGF-β. The total mast cell density was unchanged in small airways and decreased in pulmonary vessels in IPF. Both the density, as well as the percentage, of MCTC correlated positively with the degree of fibrosis. The increased density of MCTC, as well as MCTC expression of TGF-β, correlated negatively with patient lung function.
Conclusions: The present study reveals that altered mast cell populations, with increased numbers of MCTC in diseased alveolar parenchyma, represents a significant component of the histopathology in CF and IPF. The mast cell alterations correlated to the degree of tissue remodelling and to lung function parameters. Further investigations of mast cells in these diseases may open for new therapeutic strategies.
Figures


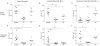



References
-
- Nilsson G, Costa J, Metcalfe D. Mast cells and basophils. 3. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

