The chloroplast division mutant caa33 of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals the crucial impact of chloroplast homeostasis on stress acclimation and retrograde plastid-to-nucleus signaling
- PMID: 22014227
- PMCID: PMC3274639
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04825.x
The chloroplast division mutant caa33 of Arabidopsis thaliana reveals the crucial impact of chloroplast homeostasis on stress acclimation and retrograde plastid-to-nucleus signaling
Abstract
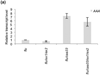
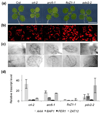
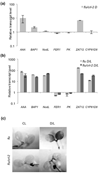
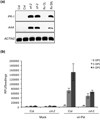
Retrograde plastid-to-nucleus signaling tightly controls and coordinates the nuclear and plastid gene expression that is required for plastid biogenesis and chloroplast activity. As chloroplasts act as sensors of environmental changes, plastid-derived signaling also modulates stress responses of plants by transferring stress-related signals and altering nuclear gene expression. Various mutant screens have been undertaken to identify constituents of plastid signaling pathways. Almost all mutations identified in these screens target plastid-specific but not extraplastidic functions. They have been suggested to define either genuine constituents of retrograde signaling pathways or components required for the synthesis of plastid signals. Here we report the characterization of the constitutive activator of AAA-ATPase (caa33) mutant, which reveals another way of how mutations that affect plastid functions may modulate retrograde plastid signaling. caa33 disturbs a plastid-specific function by impeding plastid division, and thereby perturbing plastid homeostasis. This results in preconditioning plants by activating the expression of stress genes, enhancing pathogen resistance and attenuating the capacity of the plant to respond to plastid signals. Our study reveals an intimate link between chloroplast activity and the susceptibility of the plant to stress, and emphasizes the need to consider the possible impact of preconditioning on retrograde plastid-to-nucleus signaling.
© 2011 The Authors. The Plant Journal © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of. Arabidopsis thaliana, Science. 2003;301:653–657. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez ME, Pennell RI, Meijer PJ, Ishikawa A, Dixon RA, Lamb C. Reactive oxygen intermediates mediate a systemic signal network in the establishment of plant immunity. Cell. 1998;92:773–784. - PubMed
-
- Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004;55:373–399. - PubMed
-
- Asano T, Yoshioka Y, Kurei S, Sakamoto W, Machida Y. A mutation of the CRUMPLED LEAF gene that encodes a protein localized in the outer envelope membrane of plastids affects the pattern of cell division, cell differentiation, and plastid division in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2004;38:448–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

