Ethanol alters opioid regulation of Ca(2+) influx through L-type Ca(2+) channels in PC12 cells
- PMID: 22014285
- PMCID: PMC3266970
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01631.x
Ethanol alters opioid regulation of Ca(2+) influx through L-type Ca(2+) channels in PC12 cells
Abstract
Background: Studies at the behavioral and synaptic level show that effects of ethanol on the central nervous system can involve the opioid signaling system. These interactions may alter the function of a common downstream target. In this study, we examined Ca(2+) channel function as a potential downstream target of interactions between ethanol and μ or κ opioid receptor signaling.
Methods: The studies were carried out in a model system, undifferentiated PC12 cells transfected with μ or κ opioid receptors. The PC12 cells express L-type Ca(2+) channels, which were activated by K(+) depolarization. Ca(2+) imaging was used to measure relative Ca(2+) flux during K(+) depolarization and the modulation of Ca(2+) flux by opioids and ethanol.
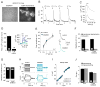
Results: Ethanol, μ receptor activation, and κ receptor activation all reduced the amplitude of the Ca(2+) signal produced by K(+) depolarization. Pretreatment with ethanol or combined treatment with ethanol and μ or κ receptor agonists caused a reduction in the amplitude of the Ca(2+) signal that was comparable to or smaller than that observed for the individual drugs alone, indicating an interaction by the drugs at a downstream target (or targets) that limited the modulation of Ca(2+) flux through L-type Ca(2+) channels.
Conclusions: These studies provide evidence for a cellular mechanism that could play an important role in ethanol regulation of synaptic transmission and behavior through interactions with the opioid signaling.
Copyright © 2011 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures


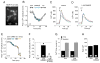



References
-
- Aguayo LG, Pancetti FC. Ethanol modulation of the gamma-aminobutyric acidA- and glycine-activated Cl- current in cultured mouse neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;270(1):61–9. - PubMed
-
- Albillos A, Carbone E, Gandia L, Garcia AG, Pollo A. Opioid inhibition of Ca2+ channel subtypes in bovine chromaffin cells: selectivity of action and voltage-dependence. Eur J Neurosci. 1996;8(8):1561–70. - PubMed
-
- Baldelli P, Hernandez-Guijo JM, Carabelli V, Novara M, Cesetti T, Andres-Mateos E, Montiel C, Carbone E. Direct and remote modulation of L-channels in chromaffin cells: distinct actions on alpha1C and alpha1D subunits? Mol Neurobiol. 2004;29(1):73–96. - PubMed
-
- Belia S, Mannucci R, Lisciarelli M, Cacchio M, Fano G. Double effect of ethanol on intracellular Ca2+ levels in undifferentiated PC12 cells. Cell Signal. 1995;7(4):389–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

