Pleural fluid soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 as a marker of bacterial infection: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 22014385
- PMCID: PMC3209451
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-11-280
Pleural fluid soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 as a marker of bacterial infection: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Pleural infection is a common clinical problem. Its successful treatment depends on rapid diagnosis and early initiation of antibiotics. The measurement of soluble triggering receptor expressed in myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) level in pleural effusions has proven to be a valuable diagnostic tool for differentiating bacterial effusions from effusions of other etiologies. Herein, we performed a meta-analysis to assess the accuracy of pleural fluid sTREM-1 in the diagnosis of bacterial infection.
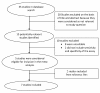
Methods: We searched Web of Knowledge and Medline from 1990 through March 2011 for studies reporting diagnostic accuracy data regarding the use of sTREM-1 in the diagnosis of bacterial pleural effusions. Pooled sensitivity and specificity and summary measures of accuracy and Q* were calculated.
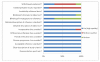
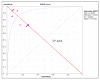
Results: Overall, the sensitivity of sTREM-1was 78% (95% CI: 72%-83%); the specificity was 84% (95% CI: 80%-87%); the positive likelihood ratio was 6.0 (95% CI: 3.3-10.7); and the negative likelihood ratio was 0.22 (95% CI: 0.12-0.40). The area under the SROC curve for sTREM-1 was 0.92. Statistical heterogeneity and inconsistency were found for sensitivity (p = 0.015, χ2 = 15.73, I2 = 61.9%), specificity (p = 0.000, χ2 = 29.90, I2 = 79.9%), positive likelihood ratio (p = 0.000, χ2 = 33.09, I2 = 81.9%), negative likelihood ratio (p = 0.008, χ2 = 17.25, I2 = 65.2%), and diagnostic odds ratio (p = 0.000, χ2 = 28.49, I2 = 78.9%). A meta-regression analysis performed showed that the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies score (p = 0.3245; RDOR, 4.34; 95% CI, 0.11 to 164.01), the Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy score (p = 0.3331; RDOR, 1.70; 95% CI, 0.44 to 6.52), lack of blinding (p = 0.7439; RDOR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.01 to 33.80), and whether the studies were prospective or retrospective studies (p = 0.2068; RDOR, 7.44; 95% CI, 0.18 to 301.17) did not affect the test accuracy. A funnel plot for publication bias suggested a remarkable trend of publication bias.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that sTREM-1 has a good diagnostic accuracy and may provide a useful adjunctive tool for the diagnosis of bacterial pleural effusions. However, further studies are needed in order to identify any differences in the diagnostic performance of sTREM-1 of parapneumonic effusions and empyemas.
Figures



References
-
- Rahman NM, Davies RJO. In: Textbook of Pleural Disease. 2. Light RW, Lee YCG, editor. London: Hodder & Stoughton; 2008. Effusions from infections: Parapneumonic effusion and empyema; pp. 341–367.
-
- Bouchon A, Dietrich J, Colonna M. Cutting edge: inflammatory responses can be triggered by TREM-1, a novel receptor expressed on neutrophils and monocytes. J Immunol. 2000;164:4991–4995. - PubMed
-
- Lourens NA, Bösenberg LH, Tintinger GR, Ker J, Fickl H, Sharp C, Van Zyl M, Anderson R. Soluble Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells in Patients With Suspected Meningitis, Peritonitis, or Pleuritis. Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice. 2008;16(3):157–162. doi: 10.1097/IPC.0b013e318167652d. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

