FoxM1 promotes β-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis
- PMID: 22014570
- PMCID: PMC3199318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.08.016
FoxM1 promotes β-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis
Abstract
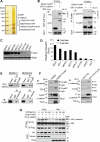
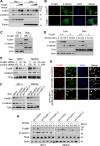
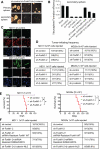
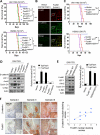
Wnt/β-catenin signaling is essential for stem cell regulation and tumorigenesis, but its molecular mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, we report that FoxM1 is a downstream component of Wnt signaling and is critical for β-catenin transcriptional function in tumor cells. Wnt3a increases the level and nuclear translocation of FoxM1, which binds directly to β-catenin and enhances β-catenin nuclear localization and transcriptional activity. Genetic deletion of FoxM1 in immortalized neural stem cells abolishes β-catenin nuclear localization. FoxM1 mutations that disrupt the FoxM1-β-catenin interaction or FoxM1 nuclear import prevent β-catenin nuclear accumulation in tumor cells. FoxM1-β-catenin interaction controls Wnt target gene expression, is required for glioma formation, and represents a mechanism for canonical Wnt signaling during tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
Location, location, location: FoxM1 mediates β-catenin nuclear translocation and promotes glioma tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell. 2011 Oct 18;20(4):415-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.10.003. Cancer Cell. 2011. PMID: 22014565
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

