Growth hormone modulates hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity in old rats
- PMID: 22015312
- PMCID: PMC3266474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.09.014
Growth hormone modulates hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity in old rats
Abstract
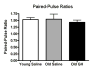
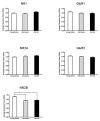
Alterations in the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate receptor (AMPA-R) and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA-R) have been documented in aged animals and may contribute to changes in hippocampal-dependent memory. Growth hormone (GH) regulates AMPA-R and NMDA-R-dependent excitatory transmission and decreases with age. Chronic GH treatment mitigates age-related cognitive decline. An in vitro CA1 hippocampal slice preparation was used to compare hippocampal excitatory transmission and plasticity in old animals treated for 6-8 months with either saline or GH. Our findings indicate that GH treatment restores NMDA-R-dependent basal synaptic transmission in old rats to young adult levels and enhances both AMPA-R-dependent basal synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation. These alterations in synaptic function occurred in the absence of changes in presynaptic function, as measured by paired-pulse ratios, the total protein levels of AMPA-R and NMDA-R subunits or in plasma or hippocampal levels of insulin-like growth factor-I. These data suggest a direct role for GH in altering age-related changes in excitatory transmission and provide a possible cellular mechanism through which GH changes the course of cognitive decline.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


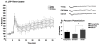
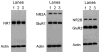

Similar articles
-
Growth hormone enhances excitatory synaptic transmission in area CA1 of rat hippocampus.J Neurophysiol. 2006 May;95(5):2962-74. doi: 10.1152/jn.00947.2005. Epub 2006 Feb 15. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16481459
-
Pregnenolone sulfate enhances long-term potentiation in CA1 in rat hippocampus slices through the modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.J Neurosci Res. 2004 Dec 1;78(5):691-701. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20332. J Neurosci Res. 2004. PMID: 15505794
-
The complementary nature of long-term depression and potentiation revealed by dual component excitatory postsynaptic potentials in hippocampal slices from young rats.Neuroscience. 1995 Oct;68(3):625-35. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00173-g. Neuroscience. 1995. PMID: 8577363
-
MPTP modulates hippocampal synaptic transmission and activity-dependent synaptic plasticity via dopamine receptors.J Neurochem. 2012 Aug;122(3):582-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07815.x. Epub 2012 Jun 22. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22651101
-
The molecular pharmacology and cell biology of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors.Pharmacol Rev. 2005 Jun;57(2):253-77. doi: 10.1124/pr.57.2.7. Pharmacol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15914469 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I alter hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission in young and old rats.Age (Dordr). 2013 Oct;35(5):1575-87. doi: 10.1007/s11357-012-9460-4. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Age (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 22851280 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of growth hormone replacement on neurological and psychomotor development. Case report.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2018 May 14;16(2):eRC3961. doi: 10.1590/S1679-45082018RC3961. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2018. PMID: 29768519 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic IGF-IRs Induce Adenosine-Mediated Inhibitory Downregulation and Improve Sensory Discrimination.J Neurosci. 2021 Jun 2;41(22):4768-4781. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0005-21.2021. Epub 2021 Apr 28. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33911021 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Hormone Alters Remapping in the Hippocampal Area CA1 in a Novel Environment.eNeuro. 2025 Feb 11;12(2):ENEURO.0237-24.2024. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0237-24.2024. Print 2025 Feb. eNeuro. 2025. PMID: 39900507 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal growth hormone modulates relational memory and the dendritic spine density in CA1.Learn Mem. 2020 Jan 16;27(2):33-44. doi: 10.1101/lm.050229.119. Print 2020 Feb. Learn Mem. 2020. PMID: 31949035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberg D. Role of growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor 1 axis in neurogenesis. Endocr Dev. 2010;17:63–76. - PubMed
-
- Aberg ND, Lind J, Isgaard J, George KH. Peripheral growth hormone induces cell proliferation in the intact adult rat brain. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010;20:264–9. - PubMed
-
- Adams MM, Smith TD, Moga D, Gallagher M, Wang Y, Wolfe BB, Rapp PR, Morrison JH. Hippocampal dependent learning ability correlates with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor levels in CA3 neurons of young and aged rats. J Comp Neurol. 2001;432:230–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

