Growth hormone modulates hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity in old rats
- PMID: 22015312
- PMCID: PMC3266474
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.09.014
Growth hormone modulates hippocampal excitatory synaptic transmission and plasticity in old rats
Abstract
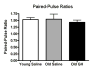
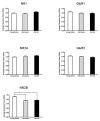
Alterations in the alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionate receptor (AMPA-R) and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA-R) have been documented in aged animals and may contribute to changes in hippocampal-dependent memory. Growth hormone (GH) regulates AMPA-R and NMDA-R-dependent excitatory transmission and decreases with age. Chronic GH treatment mitigates age-related cognitive decline. An in vitro CA1 hippocampal slice preparation was used to compare hippocampal excitatory transmission and plasticity in old animals treated for 6-8 months with either saline or GH. Our findings indicate that GH treatment restores NMDA-R-dependent basal synaptic transmission in old rats to young adult levels and enhances both AMPA-R-dependent basal synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation. These alterations in synaptic function occurred in the absence of changes in presynaptic function, as measured by paired-pulse ratios, the total protein levels of AMPA-R and NMDA-R subunits or in plasma or hippocampal levels of insulin-like growth factor-I. These data suggest a direct role for GH in altering age-related changes in excitatory transmission and provide a possible cellular mechanism through which GH changes the course of cognitive decline.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


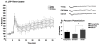
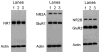

References
-
- Aberg D. Role of growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor 1 axis in neurogenesis. Endocr Dev. 2010;17:63–76. - PubMed
-
- Aberg ND, Lind J, Isgaard J, George KH. Peripheral growth hormone induces cell proliferation in the intact adult rat brain. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010;20:264–9. - PubMed
-
- Adams MM, Smith TD, Moga D, Gallagher M, Wang Y, Wolfe BB, Rapp PR, Morrison JH. Hippocampal dependent learning ability correlates with N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor levels in CA3 neurons of young and aged rats. J Comp Neurol. 2001;432:230–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

