Interleukin-8 (IL-8) over-production and autocrine cell activation are key factors in monomethylarsonous acid [MMA(III)]-induced malignant transformation of urothelial cells
- PMID: 22015448
- PMCID: PMC3254786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.10.002
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) over-production and autocrine cell activation are key factors in monomethylarsonous acid [MMA(III)]-induced malignant transformation of urothelial cells
Abstract
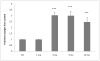
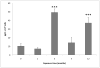
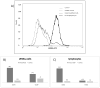
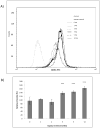
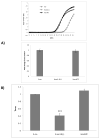
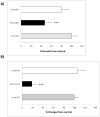
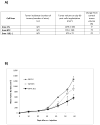
The association between chronic human exposure to arsenicals and bladder cancer development is well recognized; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms have not been fully determined. We propose that inflammatory responses can play a pathogenic role in arsenic-related bladder carcinogenesis. In previous studies, it was demonstrated that chronic exposure to 50 nM monomethylarsenous acid [MMA(III)] leads to malignant transformation of an immortalized model of urothelial cells (UROtsa), with only 3 mo of exposure necessary to trigger the transformation-related changes. In the three-month window of exposure, the cells over-expressed pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8), consistent with the sustained activation of NFKβ and AP1/c-jun, ERK2, and STAT3. IL-8 was over-expressed within hours after exposure to MMA(III), and sustained over-expression was observed during chronic exposure. In this study, we profiled IL-8 expression in UROtsa cells exposed to 50 nM MMA(III) for 1 to 5 mo. IL-8 expression was increased mainly in cells after 3 mo MMA(III) exposure, and its production was also found increased in tumors derived from these cells after heterotransplantation in SCID mice. UROtsa cells do express both receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, suggesting that autocrine cell activation could be important in cell transformation. Supporting this observation and consistent with IL-8 over-expression, CXCR1 internalization was significantly increased after three months of exposure to MMA(III). The expression of MMP-9, cyclin D1, bcl-2, and VGEF was significantly increased in cells exposed to MMA(III) for 3 mo, but these mitogen-activated kinases were significantly decreased after IL-8 gene silencing, together with a decrease in cell proliferation rate and in anchorage-independent colony formation. These results suggest a relevant role of IL-8 in MMA(III)-induced UROtsa cell transformation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Low level exposure to monomethyl arsonous acid-induced the over-production of inflammation-related cytokines and the activation of cell signals associated with tumor progression in a urothelial cell model.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Apr 15;244(2):162-73. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.12.029. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20045430 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogenic signal transduction caused by monomethylarsonous acid in human bladder cells: role in arsenic-induced carcinogenesis.Toxicol Sci. 2007 Feb;95(2):321-30. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfl160. Epub 2006 Nov 8. Toxicol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17093206
-
Monomethylarsonous acid produces irreversible events resulting in malignant transformation of a human bladder cell line following 12 weeks of low-level exposure.Toxicol Sci. 2010 Jul;116(1):44-57. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq106. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Toxicol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20375083 Free PMC article.
-
Monomethylarsonous acid induces transformation of human bladder cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006 Oct 1;216(1):69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.04.011. Epub 2006 Jun 27. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16806342 Free PMC article.
-
Immortalized human urothelial cells as a model of arsenic-induced bladder cancer.Toxicology. 2008 Jun 27;248(2-3):67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.03.020. Epub 2008 Mar 30. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18456381 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression Of Selected Pathway-Marker Genes In Human Urothelial Cells Exposed Chronically To A Non-Cytotoxic Concentration Of Monomethylarsonous Acid.Toxicol Rep. 2014;1:421-434. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.07.004. Toxicol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25177542 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin suppresses migration and invasion of transformed cells through down-regulation of C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 expression.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 1;272(1):108-16. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.05.028. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23743303 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo biloba extract attenuates the disruption of pro-and anti-inflammatory T-cell balance in peripheral blood of arsenicosis patients.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan 1;16(3):483-494. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.39351. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32015684 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy inhibition by sustained overproduction of IL6 contributes to arsenic carcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 2014 Jul 15;74(14):3740-52. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3182. Epub 2014 May 15. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24830721 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ginseng extract on the TGF-β1 signaling pathway in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jan 13;17(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1507-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28086769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arroyo M, Molina R, Martín J, López J. Tumores Urológicos. Medicine [On line] 2004;9(27) ]. Available at http://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=1253693.
-
- Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Cogliano V. Carcinogenicity of some aromatic amines, organic dyes, and related exposures. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(4):322–3. - PubMed
-
- Barton H, Messing E, Soloway M, Tomera K, Kats G, Berger Y, Shen Y, Jama On line. 2005;293(7):810–816. [cited 2008 sep 16] Available at http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/293/7/890. - PubMed
-
- Black PC, Dinney CP. Bladder cancer angiogenesis and metastasis--translation from murine model to clinical trial. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007 Dec;26(3–4):623–34. - PubMed
-
- Boffetta P. Tobacco smoking and risk of bladder cancer. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 2008;218:45–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

