MALDI imaging identifies prognostic seven-protein signature of novel tissue markers in intestinal-type gastric cancer
- PMID: 22015459
- PMCID: PMC3260837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.08.032
MALDI imaging identifies prognostic seven-protein signature of novel tissue markers in intestinal-type gastric cancer
Abstract
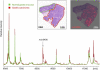
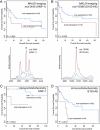
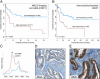
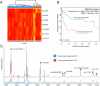
Proteomics-based approaches allow us to investigate the biology of cancer beyond genomic initiatives. We used histology-based matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) imaging mass spectrometry to identify proteins that predict disease outcome in gastric cancer after surgical resection. A total of 181 intestinal-type primary resected gastric cancer tissues from two independent patient cohorts were analyzed. Protein profiles of the discovery cohort (n = 63) were directly obtained from tumor tissue sections by MALDI imaging. A seven-protein signature was associated with an unfavorable overall survival independent of major clinical covariates. The prognostic significance of three individual proteins identified (CRIP1, HNP-1, and S100-A6) was validated immunohistochemically on tissue microarrays of an independent validation cohort (n = 118). Whereas HNP-1 and S100-A6 were found to further subdivide early-stage (Union Internationale Contre le Cancer [UICC]-I) and late-stage (UICC II and III) cancer patients into different prognostic groups, CRIP1, a protein previously unknown in gastric cancer, was confirmed as a novel and independent prognostic factor for all patients in the validation cohort. The protein pattern described here serves as a new independent indicator of patient survival complementing the previously known clinical parameters in terms of prognostic relevance. These results show that this tissue-based proteomic approach may provide clinically relevant information that might be beneficial in improving risk stratification for gastric cancer patients.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tissue-based proteomics reveals FXYD3, S100A11 and GSTM3 as novel markers for regional lymph node metastasis in colon cancer.J Pathol. 2012 Dec;228(4):459-70. doi: 10.1002/path.4021. Epub 2012 May 23. J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22430872
-
S100-A10, thioredoxin, and S100-A6 as biomarkers of papillary thyroid carcinoma with lymph node metastasis identified by MALDI imaging.J Mol Med (Berl). 2012 Feb;90(2):163-74. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0815-6. Epub 2011 Sep 22. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012. PMID: 21938494
-
Upregulated expression of annexin II is a prognostic marker for patients with gastric cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2012 Jun 8;10:103. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-10-103. World J Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22681645 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the development of protein biomarkers of oesophageal and gastric cancers.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016 Apr;10(4):532-45. doi: 10.1002/prca.201500079. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2016. PMID: 26582241 Review.
-
Proteomic and metabolic prediction of response to therapy in gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 14;20(38):13648-57. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13648. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25320503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-resolution MALDI mass spectrometric imaging of lipids in the mammalian retina.Histochem Cell Biol. 2015 May;143(5):453-62. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1303-1. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Histochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25534592
-
MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging Reveals Decreased CK5 Levels in Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinomas Compared to the Precursor Lesion Differentiated Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 8;17(7):1088. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071088. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27399691 Free PMC article.
-
High-mass-resolution MALDI mass spectrometry imaging of metabolites from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue.Nat Protoc. 2016 Aug;11(8):1428-43. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.081. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Nat Protoc. 2016. PMID: 27414759
-
Clinical Proteomics in Colorectal Cancer, a Promising Tool for Improving Personalised Medicine.Proteomes. 2018 Dec 2;6(4):49. doi: 10.3390/proteomes6040049. Proteomes. 2018. PMID: 30513835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What gastric cancer proteomic studies show about gastric carcinogenesis?Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):9991-10010. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5043-9. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27126070 Review.
References
-
- Ferlay J., Shin H.R., Bray F., Forman D., Mathers C., Parkin D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Hao Y., Xu J., Murray T., Thun M.J. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y., Zhou Y. The role of surgery in the treatment of gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2010;101:687–692. - PubMed
-
- Allgayer H., Heiss M.M., Schildberg F.W. Prognostic factors in gastric cancer. Br J Surg. 1997;84:1651–1664. - PubMed
-
- Chen C.N., Lin J.J., Chen J.J., Lee P.H., Yang C.Y., Kuo M.L., Chang K.J., Hsieh F.J. Gene expression profile predicts patient survival of gastric cancer after surgical resection. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7286–7295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

