Elevation of glutathione as a therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 22015471
- PMCID: PMC3277671
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.003
Elevation of glutathione as a therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
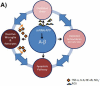
Oxidative stress has been associated with the onset and progression of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer disease (AD). AD and MCI brain and plasma display extensive oxidative stress as indexed by protein oxidation, lipid peroxidation, free radical formation, DNA oxidation, and decreased antioxidants. The most abundant endogenous antioxidant, glutathione, plays a significant role in combating oxidative stress. The ratio of oxidized to reduced glutathione is utilized as a measure of intensity of oxidative stress. Antioxidants have long been considered as an approach to slow down AD progression. In this review, we focus on the elevation on glutathione through N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) and γ-glutamylcysteine ethyl ester (GCEE) as a potential therapeutic approach for Alzheimer disease. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Antioxidants and Antioxidant Treatment in Disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




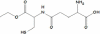
References
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease results from the cerebral accumulation and cytotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein. J Alzheimers Dis. 2001;3:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Dahlgren KN, Manelli AM, Stine WB, Jr., Baker LK, Krafft GA, LaDu MJ. Oligomeric and fibrillar species of amyloid-β peptides differentially affect neuronal viability. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:32046–32053. - PubMed
-
- Caughey B, Lansbury PT. Protofibrils, pores, fibrils, and neurodegeneration: separating the responsible protein aggregates from the innocent bystanders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:267–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

