Linoleic acid enhances angiogenesis through suppression of angiostatin induced by plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
- PMID: 22015554
- PMCID: PMC3242595
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.434
Linoleic acid enhances angiogenesis through suppression of angiostatin induced by plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
Abstract
Background: The intake of dietary fatty acids is highly correlated with the risk of various cancers. Linoleic acid (LA) is the most abundant polyunsaturated fat in the western diet, but the mechanism(s) by fatty acids such as LA modulate cancer cells is unclear. In this study, we examined the role of LA in various steps in gastric cancer progression.
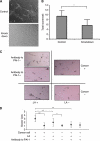
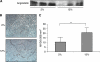
Methods: The difference in gene expression between LA-treated and untreated OCUM-2MD3 gastric carcinoma cells was examined by mRNA differential display. The involvement of candidate genes was examined by oligo- and plasmid-mediated RNA interference. Biological functions of several of these genes were examined using in vitro assays for invasion, angiogenesis, apoptosis, cell viability, and matrix digestion. Angiogenesis in vivo was measured by CD-31 immunohistochemistry and microvessel density scoring.
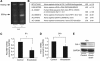
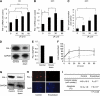
Results: LA enhanced the plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) mRNA and protein expression, which are controlled by PAI-1 mRNA-binding protein. LA-stimulated invasion depended on PAI-1. LA also enhanced angiogenesis by suppression of angiostatin, also through PAI-1. LA did not alter cell growth in culture, but increased dietary LA-enhanced tumour growth in an animal model.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that dietary LA impacts multiple steps in cancer invasion and angiogenesis, and that reducing LA in the diet may help slow cancer progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Astrup A (2005) The role of dietary fat in obesity. Sem Vasc Med 5: 40–47 - PubMed
-
- Bajou K, Maillard C, Jost M, Lijnen RH, Gils A, Declerck P, Carmeliet P, Foidart JM, Noel A (2004) Host-derived plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) concentration is critical for in vivo tumoral angiogenesis and growth. Oncogene 23: 6986–6990 - PubMed
-
- Bajou K, Noel A, Gerard RD, Masson V, Brunner N, Holst-Hansen C, Skobe M, Fusenig NE, Carmeliet P, Collen D, Foidart JM (1998) Absence of host plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 prevents cancer invasion and vascularization. Nat Med 4: 923–928 - PubMed
-
- Banfi C, Rise P, Mussoni L, Galli C, Tremoli E (1997) Linoleic acid enhances the secretion of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 by HepG2 cells. J Lipid Res 38: 860–869 - PubMed
-
- Brooks TD, Wang SW, Brunner N, Charlton PA (2004) XR5967, a novel modulator of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity, suppresses tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis in vitro. Anticancer Drugs 15: 37–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

