Transglutaminase 2: a molecular Swiss army knife
- PMID: 22015769
- PMCID: PMC3265640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.09.012
Transglutaminase 2: a molecular Swiss army knife
Abstract
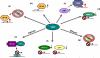
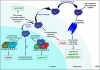
Transglutaminase 2 (TG2) is the most widely distributed member of the transglutaminase family with almost all cell types in the body expressing TG2 to varying extents. In addition to being widely expressed, TG2 is an extremely versatile protein exhibiting transamidating, protein disulphide isomerase and guanine and adenine nucleotide binding and hydrolyzing activities. TG2 can also act as a protein scaffold or linker. This unique protein also undergoes extreme conformational changes and exhibits localization diversity. Being mainly a cytosolic protein; it is also found in the nucleus, associated with the cell membrane (inner and outer side) and with the mitochondria, and also in the extracellular matrix. These different activities, conformations and localization need to be carefully considered while assessing the role of TG2 in physiological and pathological processes. For example, it is becoming evident that the role of TG2 in cell death processes is dependent upon the cell type, stimuli, subcellular localization and conformational state of the protein. In this review we discuss in depth the conformational and functional diversity of TG2 in the context of its role in numerous cellular processes. In particular, we have highlighted how differential localization, conformation and activities of TG2 may distinctly mediate cell death processes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Lai TS, Slaughter TF, Peoples KA, Hettasch JM, Greenberg CS. Regulation of human tissue transglutaminase function by magnesium-nucleotide complexes. Identification of distinct binding sites for Mg-GTP and Mg-ATP. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1776–1781. - PubMed
-
- Chen JS, Mehta K. Tissue transglutaminase: an enzyme with a split personality. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:817–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

