Perspectives and opportunities for nanomedicine in the management of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 22015921
- PMCID: PMC3623275
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd3578
Perspectives and opportunities for nanomedicine in the management of atherosclerosis
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Dec;10(12):963
Abstract
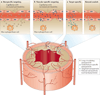
The use of nanotechnology for medical purposes--nanomedicine--has grown exponentially over the past few decades. This is exemplified by the US Food and Drug Administration's approval of several nanotherapies for various conditions, as well as the funding of nanomedical programmes worldwide. Although originally the domain of anticancer therapy, recent advances have illustrated the considerable potential of nanomedicine in the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. This Review elaborates on nanoparticle-targeting concepts in atherosclerotic disease, provides an overview of the use of nanomedicine in atherosclerosis, and discusses potential future applications and clinical benefits.
Figures

References
-
- Moghimi SM, Hunter AC, Murray JC. Nanomedicine: current status and future prospects. FASEB J. 2005;19:311–330. - PubMed
-
- Wagner V, Dullaart A, Bock AK, Zweck A. The emerging nanomedicine landscape. Nature Biotech. 2006;24:1211–1217. - PubMed
-
- Kim BY, Rutka JT, Chan WC. Nanomedicine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;363:2434–2443. - PubMed
-
- Nagarajan R, Hatton TA, editors. Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Passivation, and Functionalization. American Chemical Society; Washington DC: 2008. pp. 2–14.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

