Feasibility study of intra-patient sorafenib dose-escalation or re-escalation in patients with previously treated advanced solid tumors
- PMID: 22015991
- PMCID: PMC4131984
- DOI: 10.1007/s10637-011-9761-y
Feasibility study of intra-patient sorafenib dose-escalation or re-escalation in patients with previously treated advanced solid tumors
Abstract
Purpose: To determine if intra-patient dose escalation of the multi-targeted kinase inhibitor sorafenib is feasible in patients with advanced pretreated solid malignancies.
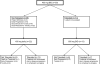
Methods: An intra-patient dose escalation scheme starting at 400 mg BID was employed in this prospective trial. Doses were escalated to 600 mg BID for the second cycle and to 800 mg BID for the third cycle in the absence of grade 3+ adverse events. In the event of grade 3+ adverse events during cycle 1, doses were reduced to 400 mg daily through cycle 2. Dose re-escalation for cycle 3 was allowed in the absence of grade 3+ adverse events during cycle 2. Further dose escalation was prohibited. The primary endpoint was the overall percentage of patients tolerating dose escalation to 600 mg BID through cycle 2 or tolerating re-escalation to 400 mg BID through cycle 3.
Results: Fifty eligible patients with various solid tumors and a median of 3 prior therapies were enrolled. Eleven patients (22%) tolerated primary dose escalation or re-escalation. Only 14 patients (28%) completed cycle 1 without dose modification or discontinuing treatment. Seven of 13 patients tolerated primary dose escalation through cycle 2. Four of 5 patients tolerated dose re-escalation through cycle 3. Reasons for escalation failure included tumor progression (42%) and adverse events (26%). Common grade 3+ adverse events included hand-foot skin reaction, hypertension, and hypophosphatemia.
Conclusions: Intra-patient dose escalation and/or re-escalation of sorafenib were not feasible in pretreated solid tumor patients. Sorafenib dose escalation remains an investigational approach.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00810394.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Is intra-patient sorafenib dose re-escalation safe and tolerable in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma?Int J Clin Oncol. 2014 Dec;19(6):1029-36. doi: 10.1007/s10147-014-0668-4. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24519322
-
Sorafenib dose escalation in treatment-naïve patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a non-randomised, open-label, Phase 2b study.BJU Int. 2017 Jun;119(6):846-853. doi: 10.1111/bju.13740. Epub 2017 Jan 9. BJU Int. 2017. PMID: 27981711 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase 1 study of sorafenib in combination with bortezomib in patients with advanced malignancies.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Oct;31(5):1201-6. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-0004-2. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23887852 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adverse events affect sorafenib efficacy in patients with recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation: experience at a single center and review of the literature.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Feb;25(2):180-6. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e328359e550. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23044808 Review.
-
Sorafenib: a review of its use in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Drugs. 2009;69(2):223-40. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969020-00006. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19228077 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuances to precision dosing strategies of targeted cancer medicines.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020 Aug;8(4):e00625. doi: 10.1002/prp2.625. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32662214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of FLT3 inhibitors in monotherapy of hematological and solid malignancies: a systemic analysis of clinical trials.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 17;15:1294668. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1294668. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38828446 Free PMC article.
-
Is intra-patient sorafenib dose re-escalation safe and tolerable in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma?Int J Clin Oncol. 2014 Dec;19(6):1029-36. doi: 10.1007/s10147-014-0668-4. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24519322
-
Inefficiencies and Patient Burdens in the Development of the Targeted Cancer Drug Sorafenib: A Systematic Review.PLoS Biol. 2017 Feb 3;15(2):e2000487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2000487. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2017. PMID: 28158308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y, Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE, Bollag G, Trail PA. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64(19):7099–7109. doi:64/19/7099 [pii] 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1443. - PubMed
-
- Awada A, Hendlisz A, Gil T, Bartholomeus S, Mano M, de Valeriola D, Strumberg D, Brendel E, Haase CG, Schwartz B, Piccart M. Phase I safety and pharmacokinetics of BAY 43-9006 administered for 21 days on/7 days off in patients with advanced, refractory solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 2005;92(10):1855–1861. doi:6602584 [pii] 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602584. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clark JW, Eder JP, Ryan D, Lathia C, Lenz HJ. Safety and pharmacokinetics of the dual action Raf kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor, BAY 43-9006, in patients with advanced, refractory solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(15):5472–5480. doi:11/15/5472 [pii] 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2658. - PubMed
-
- Moore M, Hirte HW, Siu L, Oza A, Hotte SJ, Petrenciuc O, Cihon F, Lathia C, Schwartz B. Phase I study to determine the safety and pharmacokinetics of the novel Raf kinase and VEGFR inhibitor BAY 43-9006, administered for 28 days on/7 days off in patients with advanced, refractory solid tumors. Ann Oncol. 2005;16(10):1688–1694. doi:mdi310 [pii] 10.1093/annonc/mdi310. - PubMed
-
- Strumberg D, Richly H, Hilger RA, Schleucher N, Korfee S, Tewes M, Faghih M, Brendel E, Voliotis D, Haase CG, Schwartz B, Awada A, Voigtmann R, Scheulen ME, Seeber S. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the Novel Raf kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor BAY 43-9006 in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(5):965–972. doi:JCO.2005.06.124 [pii] 10.1200/JCO.2005.06.124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

