The evolution of mammalian genomic imprinting was accompanied by the acquisition of novel CpG islands
- PMID: 22016334
- PMCID: PMC3217256
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evr104
The evolution of mammalian genomic imprinting was accompanied by the acquisition of novel CpG islands
Abstract
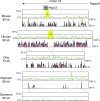
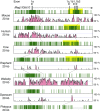
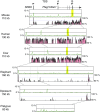
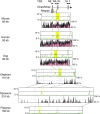
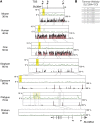
Parent-of-origin-dependent expression of imprinted genes is mostly associated with allele-specific DNA methylation of the CpG islands (CGIs) called germ line differentially methylated regions (gDMRs). Although the essential role of gDMRs for genomic imprinting has been well established, little is known about how they evolved. In several imprinted loci, the CGIs forming gDMRs may have emerged with the insertion of a retrotransposon or retrogene. To examine the generality of the hypothesis that the CGIs forming gDMRs were novel CGIs recently acquired during mammalian evolution, we reviewed the time of novel CGI emergence for all the maternal gDMR loci using the novel data analyzed in this study combined with the data from previous reports. The comparative sequence analyses using mouse, human, dog, cow, elephant, tammar, opossum, platypus, and chicken genomic sequences were carried out for Peg13, Meg1/Grb10, Plagl1/Zac1, Gnas, and Slc38a4 imprinted loci to obtain comprehensive results. The combined data showed that emergence of novel CGIs occurred universally in the maternal gDMR loci at various time points during mammalian evolution. Furthermore, the analysis of Meg1/Grb10 locus provided evidence that gradual base pair-wise sequence change was involved in the accumulation of CpG sequence, suggesting the mechanism of novel CGI emergence is more complex than the suggestion that CpG sequences originated solely by insertion of CpG-rich transposable elements. We propose that acquisition of novel CGIs was a key genomic change for the evolution of imprinting and that it usually occurred in the maternal gDMR loci.
Figures

References
-
- Duret L, Galtier N. Biased gene conversion and the evolution of mammalian genomic landscapes. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009;10:285–311. - PubMed
-
- Evans HK, Weidman JR, Cowley DO, Jirtle RL. Comparative phylogenetic analysis of blcap/nnat reveals eutherian-specific imprinted gene. Mol Biol Evol. 2005;22:1740–1748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

