Prefrontal cortex glutamate and extraversion
- PMID: 22016442
- PMCID: PMC3475356
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsr056
Prefrontal cortex glutamate and extraversion
Abstract
Extraversion is considered one of the core traits of personality. Low extraversion has been associated with increased vulnerability to affective and anxiety disorders. Brain imaging studies have linked extraversion, approach behaviour and the production of positive emotional states to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and glutamatergic neurotransmission. However, the relationship between extraversion and glutamate in the DLPFC has not been investigated so far. In order to address this issue, absolute glutamate concentrations in the DLPFC and the visual cortex as a control region were measured by 3-Tesla proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) in 29 subjects with high and low extraversion. We found increased glutamate levels in the DLPFC of introverts as compared with extraverts. The increased glutamate concentration was specific for the DLPFC and negatively associated with state anxiety. Although preliminary, results indicate altered top-down control of DLPFC due to reduced glutamate concentration as a function of extraversion. Glutamate measurement with 1H-MRS may facilitate the understanding of biological underpinnings of personality traits and psychiatric diseases associated with dysfunctions in approach behaviour and the production of positive emotional states.
Figures
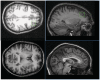

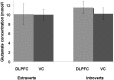

References
-
- Alvarez EO, Ruarte MB. Role of glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens on behavioural responses to novel conflictive and non-conflictive environments in the rat. Behavioural Brain Research. 2001;123:143–53. - PubMed
-
- Bagby RM, Ryder AG. Personality and the affective disorders: past efforts, current models, and future directions. Curr Psychiatry Report. 2000;2(6):465–72. - PubMed
-
- Barber AD, Carter CS. Cognitive Control Involved in Overcoming Prepotent Response Tendencies and Switching Between Tasks. Cerebral Cortex. 2005;15:899–912. - PubMed
-
- Borkenau P, Ostendorf F. NEO-Fünf-Faktoren-Inventar Hogrefe. 2008

