Substrate-induced internalization of the high-affinity choline transporter
- PMID: 22016532
- PMCID: PMC6623556
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2983-11.2011
Substrate-induced internalization of the high-affinity choline transporter
Abstract
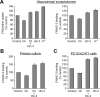
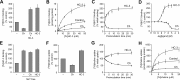
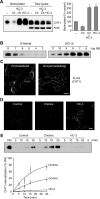
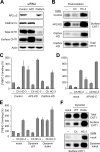
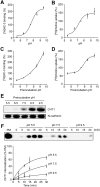
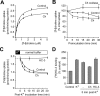
Cholinergic neurons are endowed with a high-affinity choline uptake system for efficient synthesis of acetylcholine at the presynaptic terminals. The high-affinity choline transporter CHT1 is responsible for choline uptake, the rate-limiting step in acetylcholine synthesis. However, endogenous physiological factors that affect CHT1 expression or function and consequently regulate the acetylcholine synthesis rate are essentially unknown. Here we demonstrate that extracellular substrate decreases the cell-surface expression of CHT1 in rat brain synaptosomes, primary cultures from the basal forebrain, and mammalian cell lines transfected with CHT1. Extracellular choline rapidly decreases cell-surface CHT1 expression by accelerating its internalization, a process that is mediated by a dynamin-dependent endocytosis pathway in HEK293 cells. Specific inhibitor hemicholinium-3 decreases the constitutive internalization rate and thereby increases cell-surface CHT1 expression. We also demonstrate that the constitutive internalization of CHT1 depends on extracellular pH in cultured cells. Our results collectively suggest that the internalization of CHT1 is induced by extracellular substrate, providing a novel feedback mechanism for the regulation of acetylcholine synthesis at the cholinergic presynaptic terminals.
Figures
References
-
- Bernstein EM, Quick MW. Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) transporters by extracellular GABA. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:889–895. - PubMed
-
- Chi L, Reith ME. Substrate-induced trafficking of the dopamine transporter in heterologously expressing cells and in rat striatal synaptosomal preparations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;307:729–736. - PubMed
-
- Doherty GJ, McMahon HT. Mechanisms of endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:857–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
