Activation of Rho GTPases triggers structural remodeling and functional plasticity in the adult rat visual cortex
- PMID: 22016550
- PMCID: PMC6623549
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2617-11.2011
Activation of Rho GTPases triggers structural remodeling and functional plasticity in the adult rat visual cortex
Abstract
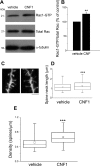
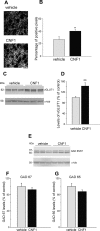
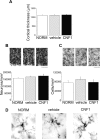
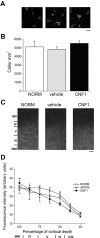
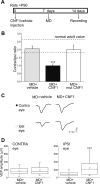
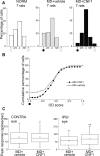
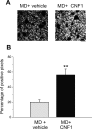
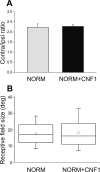
A classical example of age-dependent plasticity is ocular dominance (OD) plasticity, triggered by monocular deprivation (MD). Sensitivity of cortical circuits to a brief period of MD is maximal in juvenile animals and downregulated in adult age. It remains unclear whether a reduced potential for morphological remodeling underlies this downregulation of physiological plasticity in adulthood. Here we have tested whether stimulation of structural rearrangements is effective in promoting experience-dependent plasticity in adult age. We have exploited a bacterial protein toxin, cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1), that regulates actin dynamics and structure of neuronal processes via a persistent activation of Rho GTPases. Injection of CNF1 into the adult rat visual cortex triggered a long-lasting activation of the Rho GTPase Rac1, with a consequent increase in spine density and length in pyramidal neurons. Adult rats treated with CNF1, but not controls, showed an OD shift toward the open eye after MD. CNF1-mediated OD plasticity was selectively attributable to the enhancement of open-eye responses, whereas closed-eye inputs were unaffected. This effect correlated with an increased density of geniculocortical terminals in layer IV of monocularly deprived, CNF1-treated rats. Thus, Rho GTPase activation reinstates OD plasticity in the adult cortex via the potentiation of more active inputs from the open eye. These data establish a direct link between structural remodeling and functional plasticity and demonstrate a role for Rho GTPases in brain plasticity in vivo. The plasticizing effects of Rho GTPase activation may be exploited to promote brain repair.
Figures
References
-
- Belichenko PV, Wright EE, Belichenko NP, Masliah E, Li HH, Mobley WC, Francke U. Widespread changes in dendritic and axonal morphology in Mecp2-mutant mouse models of Rett syndrome: evidence for disruption of neuronal networks. J Comp Neurol. 2009;514:240–258. - PubMed
-
- Berardi N, Pizzorusso T, Maffei L. Critical periods during sensory development. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:138–145. - PubMed
-
- Bonhoeffer T, Yuste R. Spine motility. Phenomenology, mechanisms, and function. Neuron. 2002;35:1019–1027. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
